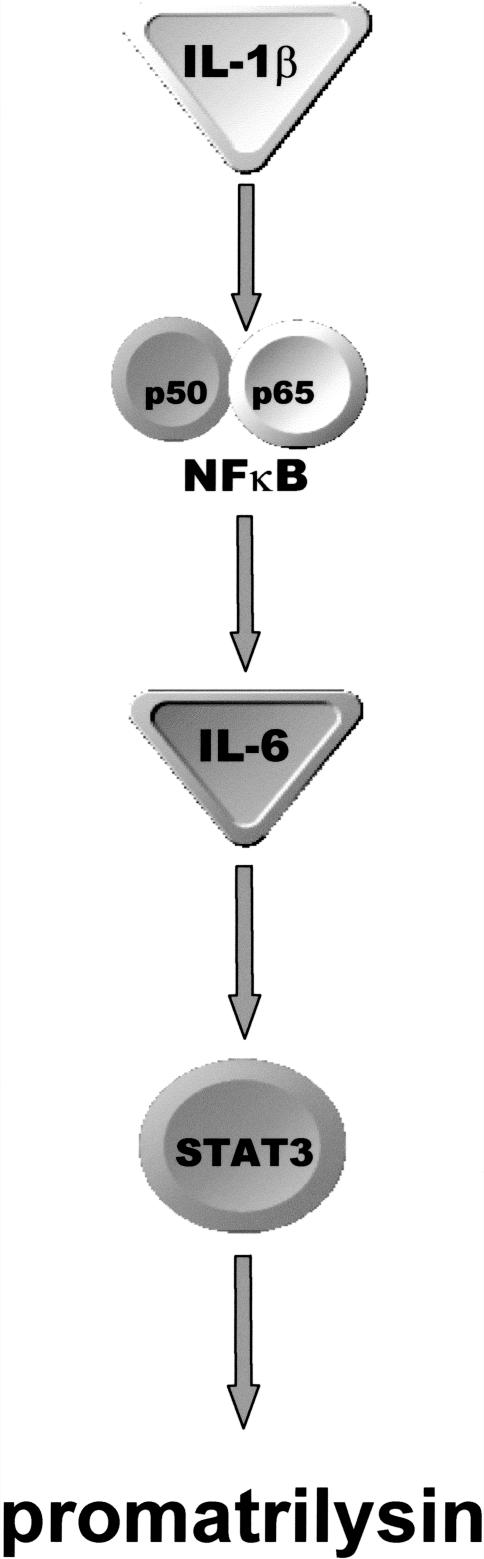
Figure 8.
Proposed IL-1β-induced promatrilysin expression signaling model. IL-1β-induced promatrilysin expression is mediated by synthesis of IL-6 through a NFκB-dependent pathway. In this model, IL-1β ligand binding to its receptor initiates the signaling cascade that results in degradation of IκB allowing nuclear translocation of the active NFκB heterodimer. Once in the nucleus, NFκB binds cis elements and induces transcription of IL-6 and other downstream effectors, which, in turn, result in transcription of the matrilysin gene. IL-6-mediated promatrilysin expression may be mediated through both autocrine and paracrine pathways depending on whether the IL-6 binds to the IL-6 receptor on the cell from which it was secreted or binds the IL-6 receptor on a neighboring cell that could be of a different type. STAT3 is activated in response to IL-6, and dominant negative STAT3 inhibits IL-6-mediated promatrilysin expression to baseline levels, which strongly indicates that STAT3 is involved in transcriptional regulation of IL-1β- and IL-6-induced promatrilysin expression.