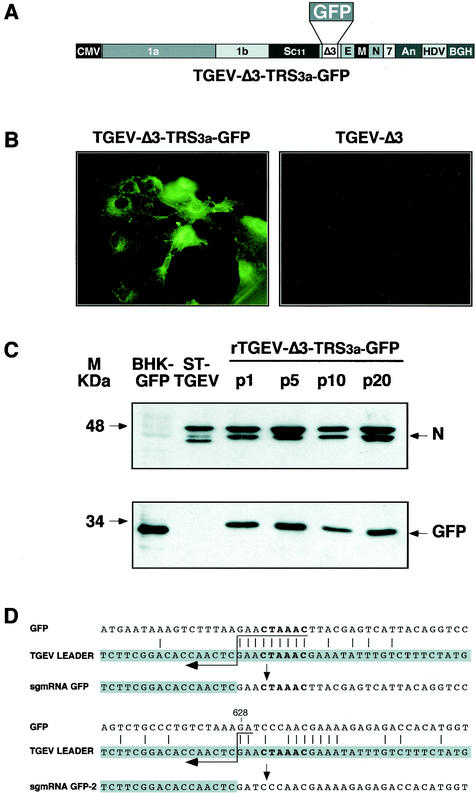
FIG. 2.
Analysis of GFP protein expressed by recombinant virus rTGEV-Δ3-TRS3a-GFP. (A) Schematic structure of the cDNA encoding the rTGEV-Δ3-TRS3a-GFP RNA with the GFP gene under the TRS of ORF 3a. The numbers and letters inside the rectangles indicate the viral genes. CMV, cytomegalovirus immediate-early promoter; An, poly(A); HDV, hepatitis delta virus ribozyme; BGH, bovine growth hormone termination and polyadenylation signals. (B) GFP expression observed by fluorescence microscopy in rTGEV-Δ3-TRS3a-GFP- but not in rTGEV-Δ3-infected swine testis cells. (C) Western blot analysis of GFP protein expressed by rTGEV-Δ3-TRS3a-GFP in infected swine testis cells. Cell lysates from passages 1 (p1), 5 (p5), 10 (p10), and 20 (p20) were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and probed with monoclonal antibodiesspecific for the viral N protein (upper panel) or GFP (lower panel). BHK-GFP, extracts from BHK cells expressing the GFP protein from the noncytopathic Sindbis virus replicon were used as a positive control. ST-TGEV, extracts from TGEV-infected swine testis cells. The molecular mass is indicated on the left. (D) Nucleotide identity between the leader RNA of TGEV and the genomic sequences of rTGEV-Δ3-TRS3a-GFP surrounding the core sequence of TRS3a (upper scheme) or the noncanonical junction site in the 3′ half of the GFP gene (lower scheme). The leader region (shaded nucleotides) includes the canonical core sequence (in bold type) and the 20 immediately upstream and downstream nucleotides. Leader-body common nucleotides are indicated by vertical bars. Postulated polymerase strand switching during minus-strand synthesis is indicated by the arrow. The jump during discontinuous transcription could have occurred anywhere within the consecutive nucleotides underlined by the tail of the arrow. The number above the genomic sequence indicates the position relative to the start of the GFP gene.