FIG. 3.
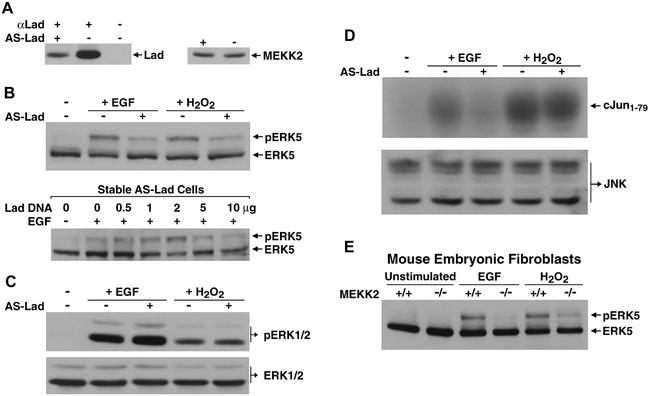
Requirement of Lad and MEKK2 in specific MAPK signaling. (A) AS-Lad specifically inhibited endogenous Lad expression. CCL64 cells were stably transfected with a DNA construct encoding AS-Lad (from −51 to +345 relative to the ATG start site) or control mock vector. Left panel: Cell lysates were incubated with preimmune or Lad antiserum, and immunoprecipitates were Western blotted with anti-Lad. Right panel: Cell lysates were blotted with anti-MEKK2. (B) Lad is required for ERK5 activation by EGF and H2O2. ERK5 activation was analyzed in a gel-shift assay based on the previous finding that activated ERK5 has a characteristic reduced mobility on SDS-polyacrylamide gels (upper panel). AS-Lad inhibition of EGF-stimulated ERK5 activation can be reversed by transient expression of Lad (lower panel). Increasing amounts of Lad were transiently expressed for 6 h in AS-Lad cells, which were subsequently treated with EGF after 3 h of serum starvation. ERK5 activities were determined by Western blotting. (C) Lad is dispensable for ERK1/2 signaling. EGF- or H2O2-treated AS-Lad or mock-transfected cells were analyzed for ERK1/2 responses by Western blotting using a phospho-ERK1/2-specific antibody (upper panel). Immunoblotting cell lysates with anti-ERK1/2 showed no difference in endogenous ERK1/2 expression (lower panel). (D) Lad contributes to EGF- but not H2O2-induced JNK activation. Endogenous JNK was pulled down with GST-cJun1-79 and used in an in vitro kinase assay (upper panel). Blotting with an anti-JNK antibody showed that AS-Lad does not affect JNK expression (lower panel). (E) MEKK2 is required for EGF and H2O2 activation of ERK5. MEKK2-knockout MEFs or wild-type MEFs were stimulated as indicated. Analysis of ERK5 activities was as described in the legend for panel B.