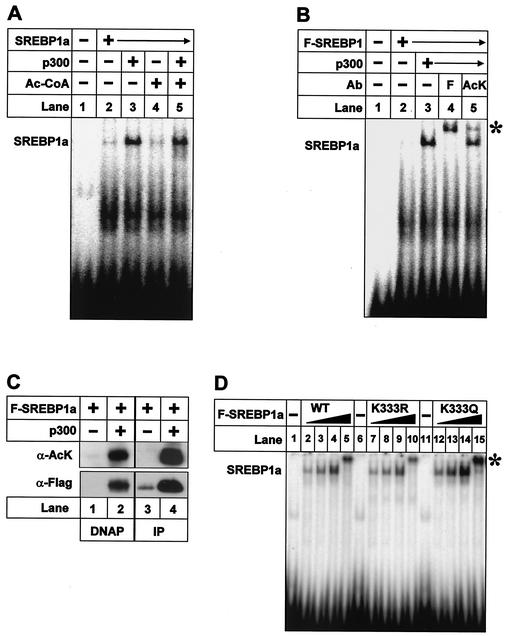
FIG. 6.
Acetylated SREBP1a binds DNA. (A) Recombinant SREBP1a was used in EMSAs with a 32P-labeled probe containing the SRE-1 sequence from the LDLR promoter. Where indicated, SREBP1a was incubated with p300 (lane 3), acetyl-CoA (Ac-CoA; lane 4), or p300 plus acetyl-CoA (lane 5) prior to the EMSA. (B) Flag-tagged wild-type SREBP1a was expressed in 293T cells in the absence (lane 2) or presence of p300-HA (lanes 3 to 5). Thirty-six hours after transfection, nuclear extracts were prepared and used in EMSA with a 32P-labeled probe containing the SRE-1 sequence from the LDLR promoter. Where indicated, anti-Flag (F; lane 4) or anti-acetyl lysine (AcK; lane 5) antibodies were included in the assay. ∗, supershifted complexes. (C) Nuclear extracts were prepared from 293T cells transfected as in panel B and used in DNAP assays with the SRE-1 sequence from the LDLR promoter (lanes 1 and 2) or immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Flag antibodies (lanes 3 and 4). The levels and acetylation of SREBP1a were determined by Western blotting using anti-Flag (α-Flag) and anti-acetyl lysine (α-AcK) antibodies, respectively. (D) Increasing amounts of in vitro-translated Flag-SREBP1a, the wild type (WT) and the indicated mutants, were used in EMSAs with a 32P-labeled probe containing the SRE-1 sequence from the LDLR promoter. The SREBP1a-DNA complexes were supershifted with anti-Flag antibodies (lanes 5, 10, and 15; asterisk).