FIG. 5.
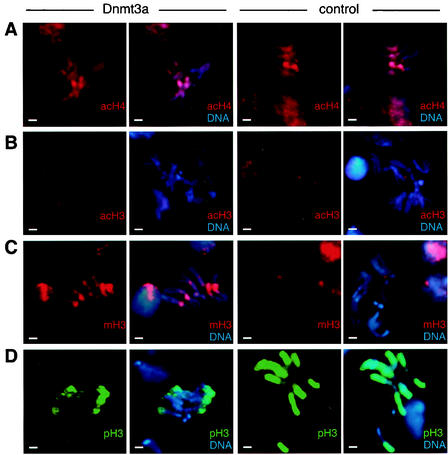
DNA hypermethylation causes changes in epigenetic histone modifications. (A) Immunodetection of acetylated histone H4 (acH4) on chromosome preparations from larval neuroblasts. There was no detectable difference between flies expressing full-length or deleted Dnmt3a protein. (B) Similarly, H3-K9 acetylation (acH3) was found to be very low on mitotic chromosomes and did not change upon DNA methylation. (C) Immunodetection of K9-methylated histone H3 (mH3). Chromosomes from Dnmt3a-overexpressing flies showed a strongly increased level of H3 methylation compared to controls. The majority of K9-methylated H3 staining was located in pericentromeric heterochromatin. (D) Phosphorylation of H3-S10 (pH3) was strongly reduced on chromosomes from Dnmt3a-overexpressing flies. Only the telomere-proximal regions of the chromosome arms remained stained. Control chromosomes showed widespread and homogeneous phosphorylation of H3. Bars, 2 μm.