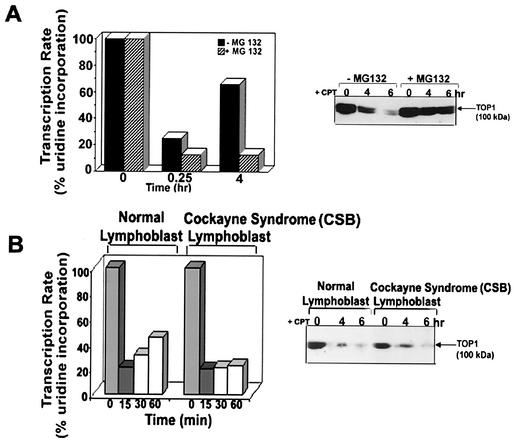
FIG. 4.
Transcription recovery requires Top I degradation and functional TCR. (A) Transcription recovery is blocked by the 26S proteasome inhibitor MG132. (Left) V79 cells were pretreated with MG132 for 1 h, followed by CPT treatment for various periods. The transcription rate was measured (by 15 min of pulse-labeling with [3H]uridine) at different times following CPT treatment. (Right) CPT-induced degradation of Top I is blocked by MG132. V79 cells were pretreated with MG132 (1 μM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with CPT (25 μM) for 4 and 6 h. Cells were then incubated in the absence of CPT but in the presence of MG132 for 30 min at 37°C to reverse the cleavable complexes. Cells were lysed by the alkaline lysis procedure. Cell lysates were neutralized, treated with S7 nuclease, and analyzed by immunoblotting. Immunodetection of Top I was done by the ECL Western procedure as described for Fig. 1A. (B) Transcription recovery in CSB cells treated with CPT. (Left) Wild-type lymphoblast GM01953C and CSB lymphoblast GM01712B cells were treated with CPT (25 μM). Transcription rates were measured at different times by 15 min of pulse-labeling with [3H]uridine following CPT treatment. (Right) Degradation of Top I-DNA covalent complexes in wild-type and CSA cells. Normal GM01953C cells and CSB GM01712B cells were treated with 25 μM CPT for various times. Reversal of cleavable complexes and immunodetection of Top I were carried out as described for Fig. 1A.