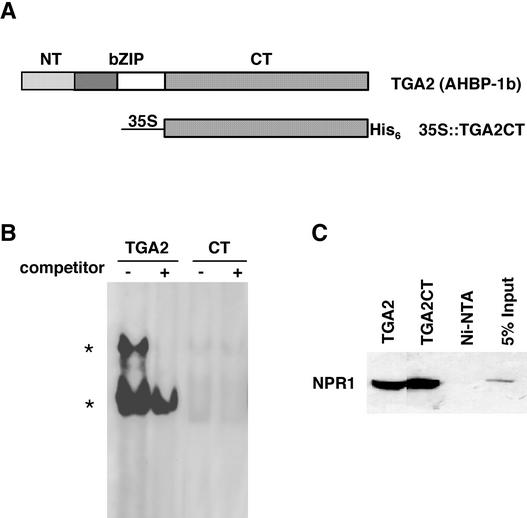
Figure 1.
In Vitro Characterization of TGA2CT.
(A) TGA2 and 35S::TGA2CT. The TGA2 transcription factor consists of the NT domain (amino acids 1 to 46), the bZIP domain (amino acids 47 to 94), and the CT domain (amino acids 95 to 330). TGA2CT was put under the control of the 35S CaMV, and the resulting protein was tagged with a His6 tag at the C terminus.
(B) GMSA. The recombinant proteins were purified from E. coli. The proteins (0.1 μg of TGA2 or 1 μg of TGA2CT [CT]) were incubated with 32P-labeled as-1 element (4 × 104 cpm) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 5 ng of unlabeled probe as a competitor. The TGA2–as-1 complexes are indicated by asterisks.
(C) In vitro copurification analysis. Purified recombinant TGA proteins (5 μg) were mixed with 20 μL of protein extract from an NPR1-expressing insect cell line (Zhang et al., 1999) and loaded onto Ni-NTA columns. The His-tagged TGA proteins and their interactors were eluted, and the eluates were run on an SDS-PAGE gel. As a control, the NPR1 extract alone was loaded onto an Ni-NTA column, and the eluate was loaded onto the gel. As an additional control, 1 μL of the NPR1 extract (5% input) was applied directly to the gel. The NPR1 protein that coeluted with the TGA factors was detected by protein gel blot analysis using an antibody against NPR1 (Cao et al., 1998).