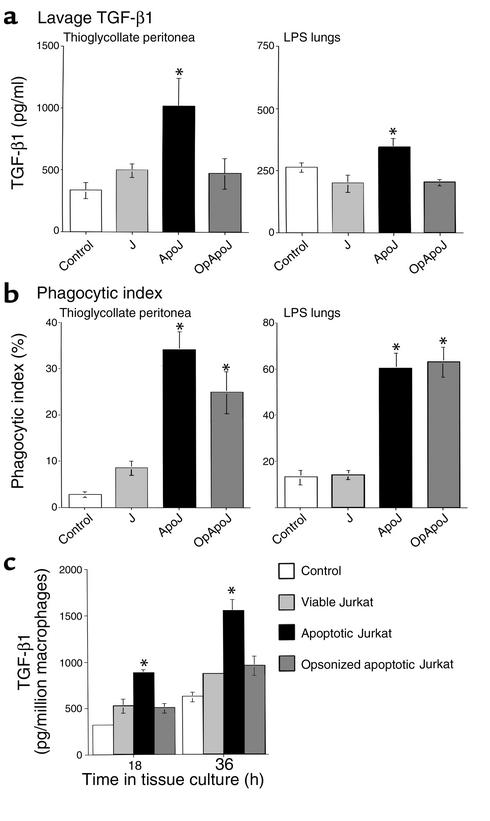
Figure 2.
In vivo secretion of TGF-β1 in inflamed peritonea and lungs is increased by apoptotic cell clearance. After intraperitoneal or endotracheal instillation of HBSS alone (control), viable Jurkat T cells (J), apoptotic Jurkat T cells (ApoJ), or opsonized apoptotic Jurkat T cells (OpApoJ) into LPS-stimulated lungs (2 days old) and thioglycollate-stimulated peritonea (3 days old), lavage supernatants collected after 4 hours and 1 hour, respectively, of incubation were assayed for TGF-β1 by ELISA. (a) ApoJ induced TGF-β1 when compared with control, while J and OpApoJ did not. (b) Phagocytic index (PI = number of apoptotic bodies/200 macrophages × 100) of peritoneal or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cytospins showed low uptake in the control and J, and increased PI for both ApoJ and OpApoJ. (c) The TPMφ’s were isolated and cultured after in vivo instillation of cells; induction of TGF-β1 in the macrophages treated with apoptotic Jurkat T cells persisted for 18 and 36 hours in tissue culture, when compared with that in viable and opsonized apoptotic Jurkat T cells. (a) *P < 0.05, n = 6, ± SD; (b) *P < 0.05, n ≥ 12, ± SD; (c) *P < 0.05, n ≥ 10, ± SD.