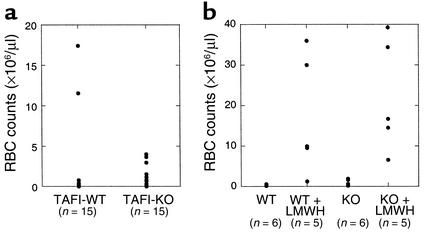
Figure 2.
Tail bleeding. Wild-type mice and TAFI-deficient mice were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital and a 1-mm segment was amputated from the tip of the tail, as described in Methods. The tail was immediately immersed in saline at 37°C. The amount of red blood cells released from the tail wound into saline was determined with a Baker 9120+CP Cell Counter (a). For tail bleeding in the presence of low-molecular-weight heparin, mice were injected with Lovenox (3 mg/kg body weight) in the tail vein 2 minutes before tail transection, and the amount of blood loss was measured similarly (b). The number of animals used in each group is indicated in parentheses. RBC, red blood cell; WT, wild-type; KO, knockout.