Fig. 3.
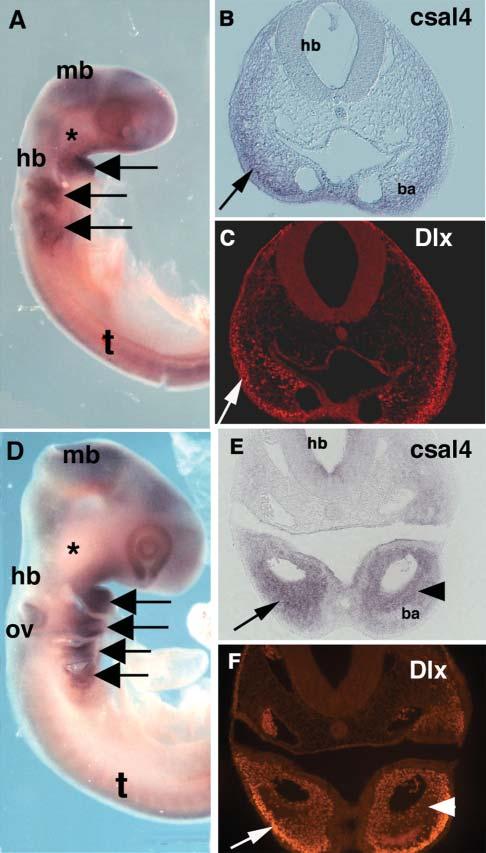
Neural crest cells in the branchial arches express csal4. (A) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of stage-14-chicken embryo with csal4 probe. A strong signal can be seen in the branchial arches (arrows) but there is no detectable signal at site of the trigeminal ganglia (asterisk). (B) Section through the region of the hindbrain of the embryo in A. Neural crest in the branchial arch (arrow) expresses csal4. (C) Same section as in B, stained with pan-Dlx antibody. Although not all Dlx-expressing cells express csal4, there is an overlapping population that expresses both (arrows). (D) Whole mount in situ hybridization of a stage-15-chicken embryo with csal4 probe. All the branchial arches (arrows) but not the trigeminal ganglia (asterisk) express csal4 strongly.(E) Section through the embryo in D showing extensive expression of csal4 throughout the branchial arch (arrow) with highest levels in the core (arrowhead). (F) Section in E stained with pan-Dlx antibody. Although there is an overlapping population that expresses both csal4 and Dlx protein, the highest level of Dlx expression (arrow) is distal to the region in which csal4 expression is highest (arrowhead). Abbreviations: ba, branchial arch; hb, hindbrain; mb, midbrain; ov, otic vesicle; t, trunk.
