Abstract
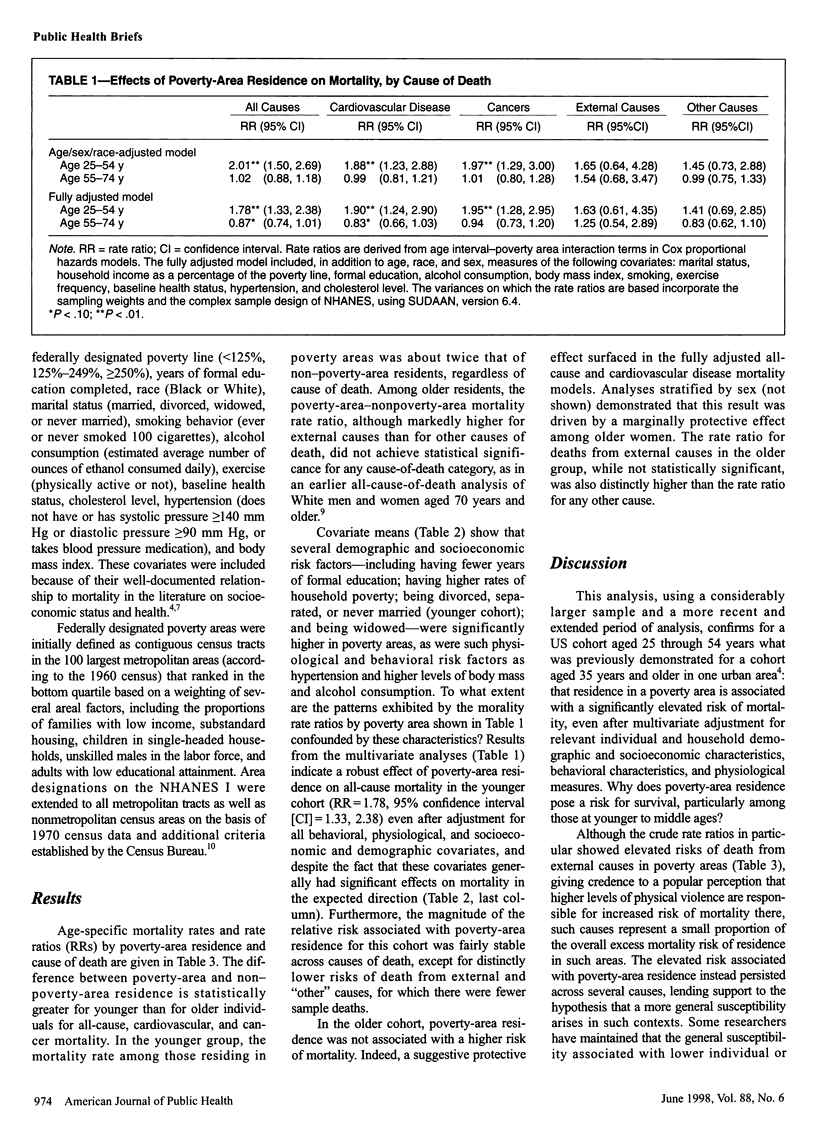
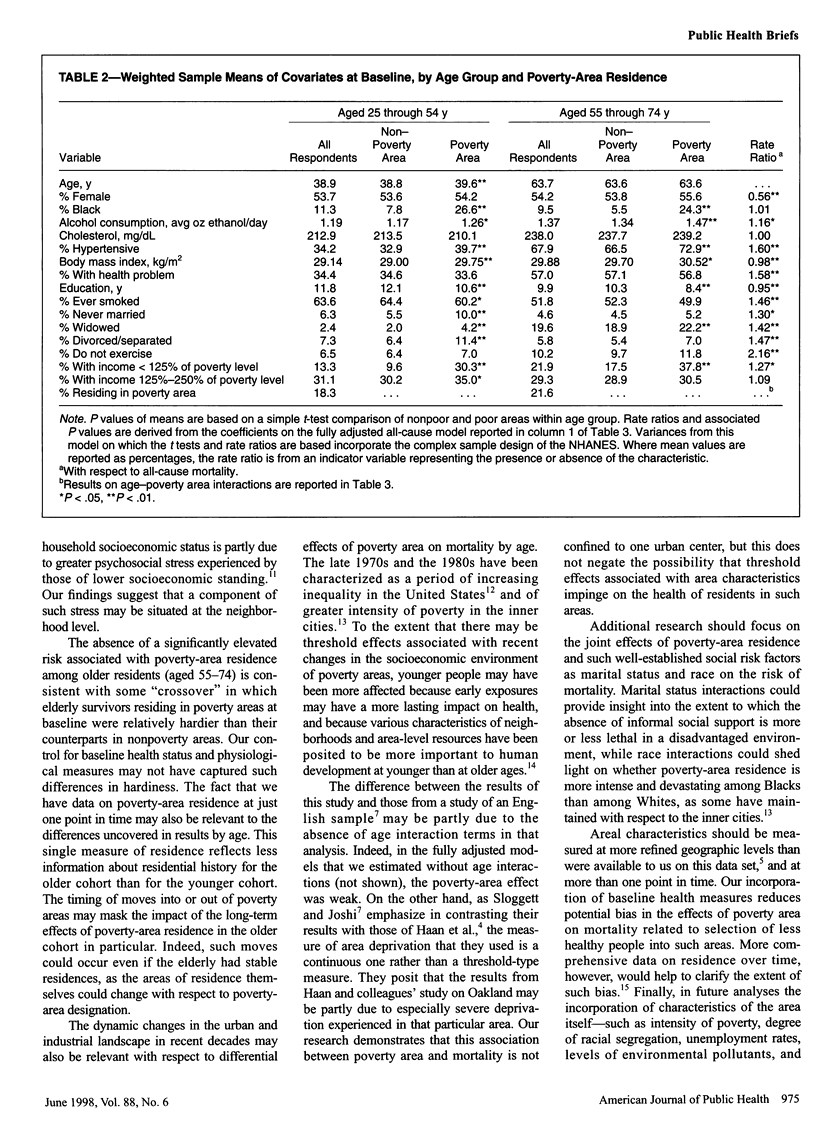
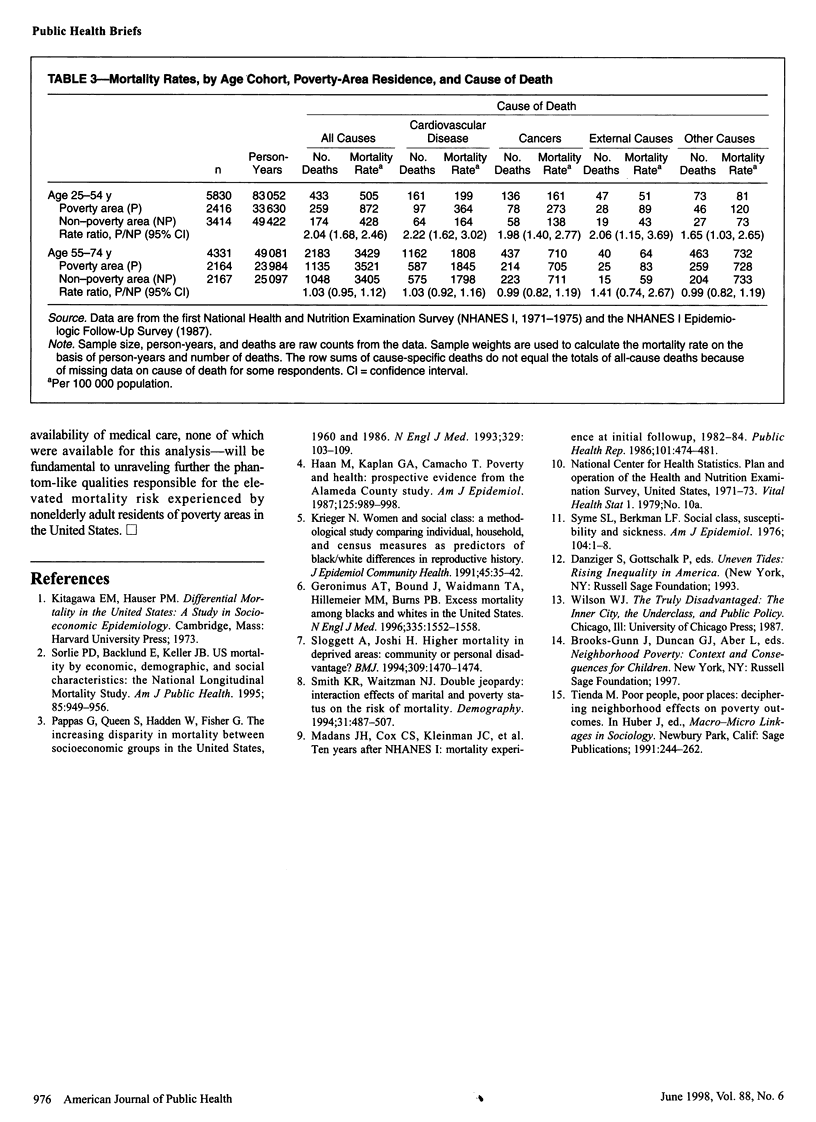
OBJECTIVES: The purpose of the study was to conduct a national multivariate analysis on poverty-area residence and mortality in the United States. METHODS: Proportional hazards analyses were performed of the effect of poverty-area residence on the risk of mortality among adult examinees in the 1971 through 1974 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey who were followed through 1987. RESULTS: Poverty-area residence was associated with significantly elevated risk of all-cause mortality (rate ratio = 1.78, 95% confidence interval = 1.33, 2.38) and some cause-specific mortality among those aged 25 through 54 years, but not among those aged 55 through 74 years, at baseline after adjustment for several individual and household characteristics. CONCLUSIONS: Residence in poverty areas contributes to socioeconomic gradients in mortality among nonelderly adults in the United States.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Geronimus A. T., Bound J., Waidmann T. A., Hillemeier M. M., Burns P. B. Excess mortality among blacks and whites in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1996 Nov 21;335(21):1552–1558. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199611213352102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haan M., Kaplan G. A., Camacho T. Poverty and health. Prospective evidence from the Alameda County Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Jun;125(6):989–998. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger N. Women and social class: a methodological study comparing individual, household, and census measures as predictors of black/white differences in reproductive history. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1991 Mar;45(1):35–42. doi: 10.1136/jech.45.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madans J. H., Cox C. S., Kleinman J. C., Makuc D., Feldman J. J., Finucane F. F., Barbano H. E., Cornoni-Huntley J. 10 years after NHANES I: mortality experience at initial followup, 1982-84. Public Health Rep. 1986 Sep-Oct;101(5):474–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas G., Queen S., Hadden W., Fisher G. The increasing disparity in mortality between socioeconomic groups in the United States, 1960 and 1986. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 8;329(2):103–109. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307083290207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rate W. R., Solin L. J. Mediastinoscopy incision site metastasis. Implications for radiotherapeutic treatment. Cancer. 1989 Jan 1;63(1):68–69. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890101)63:1<68::aid-cncr2820630111>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloggett A., Joshi H. Higher mortality in deprived areas: community or personal disadvantage? BMJ. 1994 Dec 3;309(6967):1470–1474. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6967.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. R., Waitzman N. J. Double jeopardy: interaction effects of marital and poverty status on the risk of mortality. Demography. 1994 Aug;31(3):487–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorlie P. D., Backlund E., Keller J. B. US mortality by economic, demographic, and social characteristics: the National Longitudinal Mortality Study. Am J Public Health. 1995 Jul;85(7):949–956. doi: 10.2105/ajph.85.7.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syme S. L., Berkman L. F. Social class, susceptibility and sickness. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Jul;104(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


