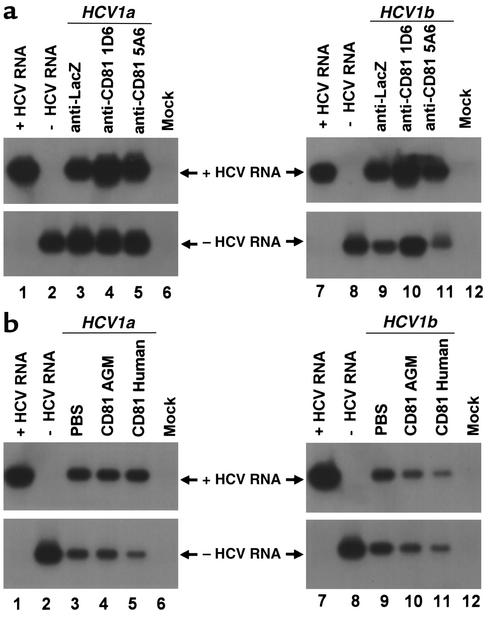
Figure 7.
HCV infection of primary Tupaia hepatocytes in the presence of anti-CD81 and soluble CD81-LEL. (a) Hepatocytes were incubated with anti-CD81 antibodies (5A6 and 1D6) at saturating conditions (10 μg/ml) or with control antibody (anti-LacZ, 10 μg/ml) 1 hour prior to the addition of HCV serum as described in Methods. HCV infection was determined by RT-PCR of cellular positive- and negative-strand HCV RNA on day 5 after incubation with RNA-positive serum HCV of genotypes 1a (50 μl, moi 0.2, lanes 3–5) and 1b (50 μl, moi 0.1, lanes 9–11) as described above. Strand specificity of RT-PCR was assessed by RT-PCR of 10 fg of in vitro–synthesized positive- (lanes 1 and 7) and negative-strand HCV RNA (lanes 2 and 8). (b) Serum-derived HCV was mixed with PBS (lanes 3 and 9), soluble CD81-LEL derived from African green monkey (AGM) (50 μg/ml; lanes 4 and 10), or human CD81-LEL (50 μg/ml; lanes 5 and 11), and incubated for 1 hour in PBS. Subsequently, HCV-CD81 complexes were added to the hepatocytes as described in Methods. Infection of hepatocytes was assessed as described above.