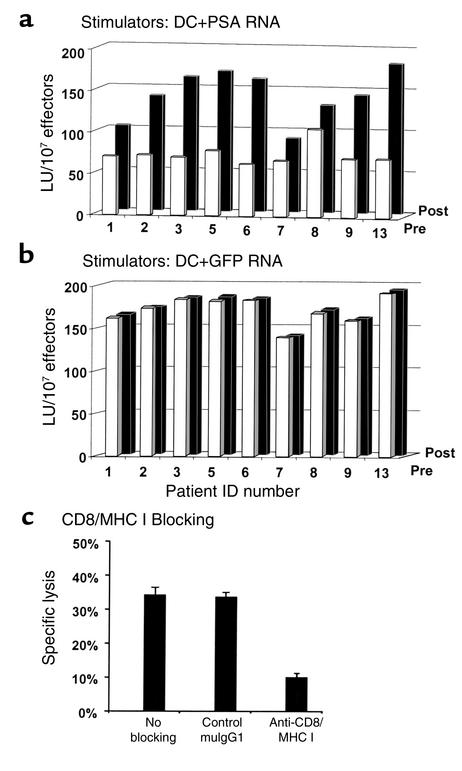
Figure 3.
Functional properties of the in vivo–generated PSA-specific CTLs. PBMCs derived from study patients at baseline (white bars) or after immunotherapy (black bars) were stimulated twice with PSA RNA (a) or GFP RNA–transfected DCs (b). Using standard 51Cr microcytotoxicity assays, lytic activities against PSA RNA– or GFP RNA–transfected DC targets were calculated. (c) Experiments in which MHC class I– or CD8-specific mAb’s were used to inhibit recognition and lysis of PSA RNA-loaded DC targets. The addition of these mAb but not isotype control mAb (Control mulgG1) during incubation of effector and target cells (40:1 E/T ratio) resulted in significant inhibition of PSA-specific cytolytic activity, suggesting that the observed responses are predominately mediated by MHC class I–restricted CD8 CTL.