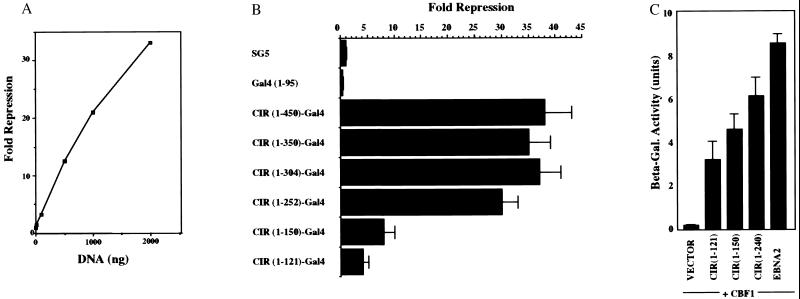
Figure 3.
Mapping CIR domains required for repression and CBF1 interaction. (A) Transient-expression assay performed in a dose-response format in HeLa cells cotransfected with a 5xGal4BS–TKCAT reporter (5 μg), a TK-Luc control (1 μg), and increasing amounts of a CIR(1–450)-Gal4(1–95) expression vector. CIR represses reporter-gene expression in a dose-responsive manner. CAT, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (B) The repression domain is located within CIR amino acids 1–252. Transient-expression assay in HeLa cells cotransfected with 5xGal4BS–TKCAT reporter (5 μg), TK-Luc control (1 μg), and 2 μg of plasmids expressing the indicated CIR–Gal4(1–95) fusion constructions. The results shown are an average of three experiments, with the SD indicated. (C) The CBF1 interaction domain is also located within an N-terminal domain. Yeast two-hybrid assay using β-galactosidase induction as a measure of interaction. CIR(1–121), CIR(1–150), CIR(1–252), and EBNA2 (252–425) were expressed as Gal4ACT fusions, and CBF1 was expressed as a Gal4DBD fusion. The EBNA2–CBF1 pairing served as a positive control for a strong interaction. The results shown are an average of three experiments, with the SD indicated.