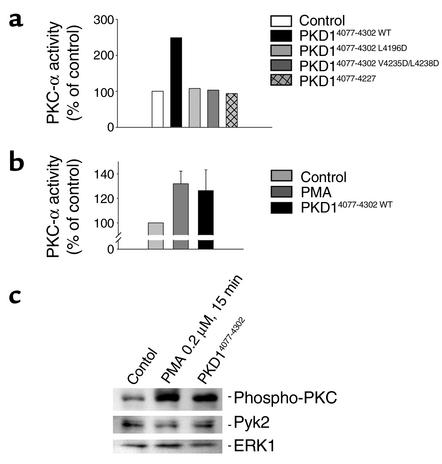
Figure 11.
Activation of protein kinase C-α requires the integrity of the heptad repeats of the C-terminal domain of polycystin-1. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with wild-type PKC-α and expression plasmids as indicated. The activity of immunoprecipitated PKC-α was determined by in vitro kinase assays. The C-terminal domain of polycystin-1 triggered a 270% activation of PKC-α, while polycystin-1, containing the L4196D or V4235D/L4238D mutations, completely lost the ability to activate PKC-α. (b) The C-terminal domain of polycystin-1 activates endogenous PKC-α in IMCD cells. Endogenous PKC-α was immunoprecipitated using an isoform specific antibody, and subjected to in vitro kinase assays. The increase in PKC-α activity by the C-terminal domain of polycystin-1 was comparable to the activation triggered by PMA (0.2 μM for 15 minutes). (c) Activation of endogenous PKC isoforms by the C-terminal domain of polycystin-1 was confirmed using a phospho-specific PKC antiserum. To control for loading, the Western blot was reprobed with antisera that detect the total amounts of the protein kinases ERK1 and Pyk2.