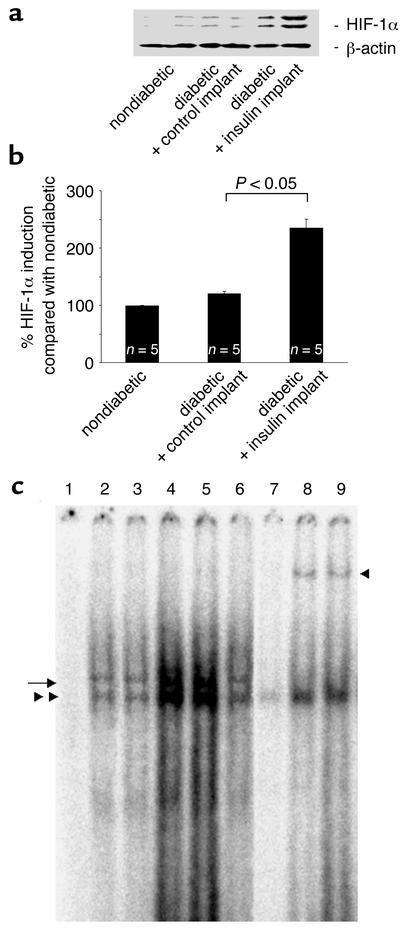
Figure 4.
(a) Nuclear HIF-1α expression levels in the retinae of nondiabetic and diabetic rats treated with control and insulin implants. Following normalization to β-actin, the HIF-1α protein levels in the diabetic animals increased 19.9% compared with the nondiabetic animals (100 ± 0.62 vs. 119.6 ± 4.26, n = 5, P < 0.05). The HIF-1α content increased an additional 96.4% in the diabetic animals treated with the insulin implants (235.04 ± 15.37, n = 5, P < 0.05 vs. control implants). (b) Western blot analysis of HIF-1α retinal nuclear protein levels in nondiabetic and diabetic rats treated with control or insulin implants. Insulin treatment upregulates the HIF-1α nuclear content in the diabetic rats. (c) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay for HIF-1α in retinal nuclear extracts from nondiabetic rats and diabetic rats treated with control or insulin implants. The extracts were incubated with labeled HRE-containing oligonucleotides from the VEGF promoter. Lane 1, free probe; lane 2, nondiabetic rats; lane 3, diabetic rats; lanes 4 and 5, insulin implant–treated rats; lane 6, control implant–treated rats; lane 7, competition with the cold oligonucleotide; lanes 8 and 9, incubation with the HIF-1α antibody (n = 5 retinae per lane for all). The markings on the left indicate the HIF-1α complexes. The marking on the right identifies the supershifted bands following exposure to the HIF-1α antibody.