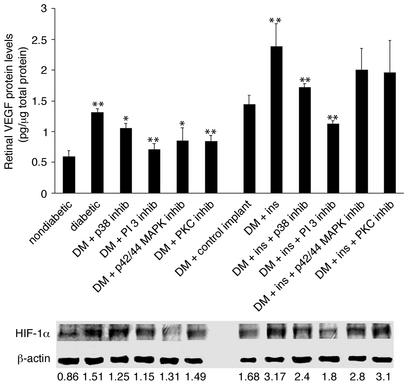
Figure 5.
Upper panel: Retinal VEGF protein levels in diabetic (DM) animals with and without insulin and kinase inhibitors. Treatment with inhibitors of p38 MAPK, PI 3-kinase, p42/p44, or PKC suppressed diabetes-induced upregulation of retinal VEGF protein levels (from 1.3 to 1.02, 0.71, 0.85, and 0.84 pg/mg of total retinal protein, respectively; n = 8, P < 0.001). Inhibition of p38 MAPK and PI 3-kinase suppressed insulin-induced upregulation of retinal VEGF levels in vivo (from 2.38 to 1.72 and 1.12 pg/mg total retinal protein, respectively; n = 8, P < 0.001). Treatment with PKC or p42/p44 MAPK inhibitors failed to suppress insulin-induced upregulation of retinal VEGF protein levels (1.96 and 2.0 pg/mg total retinal protein, respectively; n = 8, P > 0.05). Asterisks denote statistically significant results (*P < 0.005, **P < 0.001). Lower panel: Retinal HIF-1α protein levels in diabetic animals with and without insulin and kinase inhibitors. Treatment with p38 MAPK, p42/p44 MAPK, and PI 3-kinase inhibitors reduced the diabetes-induced upregulation of HIF-1α protein levels (HIF-1α/β-actin ratio from 1.509 to 1.25, 1.31, and 1.15, respectively; n = 4, P < 0.001), whereas PKC inhibition did not have a significant effect (to 1.49, n = 4, P > 0.05). Treatment with p38 MAPK and PI 3-kinase inhibitors suppressed insulin-induced upregulation of the retinal HIF-1α levels (to 2.4 and 1.8, respectively; n = 4, P < 0.001). Treatment with either the p42/p44 MAPK or the PKC inhibitors failed to alter levels (2.8 and 3.1, respectively; n = 4, P > 0.05).