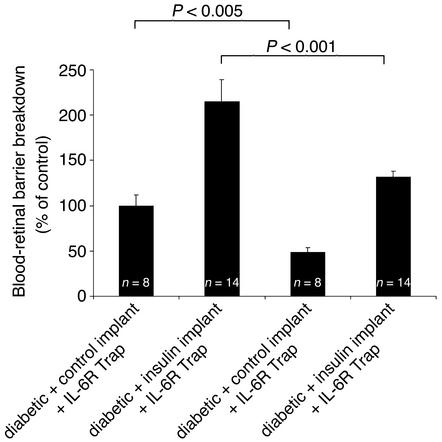
Figure 7.
VEGF inhibition reverses the blood-retinal barrier breakdown increases associated with acute intensive insulin therapy. VEGF TrapA40 reduced blood-retinal barrier breakdown in the diabetic rats treated with control implants by 42.3% (diabetic + control implant + VEGF TrapA40 vs. Inactive IL-6R Trap, n = 8, P < 0.005), and in the diabetic rats treated with the insulin implants by 50.3% (diabetic + insulin implant + VEGF TrapA40 vs. IL-6R Trap, n = 14, P < 0.001).