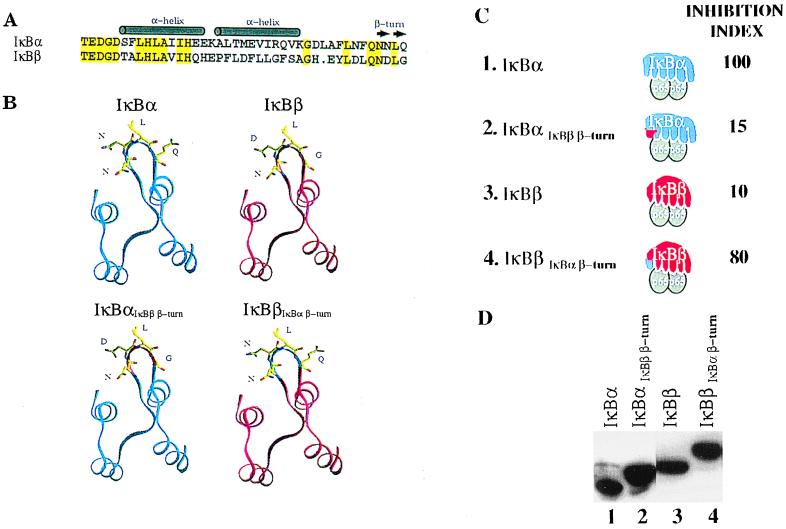
Figure 3.
Swapping a putative β-turn between IκBα and IκBβ switches their inhibitory activities. (A) Sequence alignment and secondary structure prediction of the first ankyrin repeat of IκBα and IκBβ. Identical amino acids are indicated in yellow. (B) Model building of the first ankyrin repeat of IκBα and IκBβ performed by using O (28). Coordinates for GABPβ (21) and 53BP2 (19) were obtained from the Protein Data Bank (29). When modeling IκBα and IκBβ, the same backbone dihedrals were used and side chain rotamers were built such that the rotamer matched that of the crystal structures. (C) P19 cells were transfected as outlined in Fig. 2 along with expression vectors encoding the IκBαIκBβ β-turn and IκBβIκBα β-turn inhibitors. The inhibition index was derived from five independent experiments and the variability was less than 20%. (D) Shown is a Western blot verifying the comparable expression of the indicated IκB proteins after transfection. The slightly larger size (2 kDa) of the swapped constructs compared with their wild-type counterparts is caused by the presence of the six histidine tag moiety at their amino termini.