Abstract
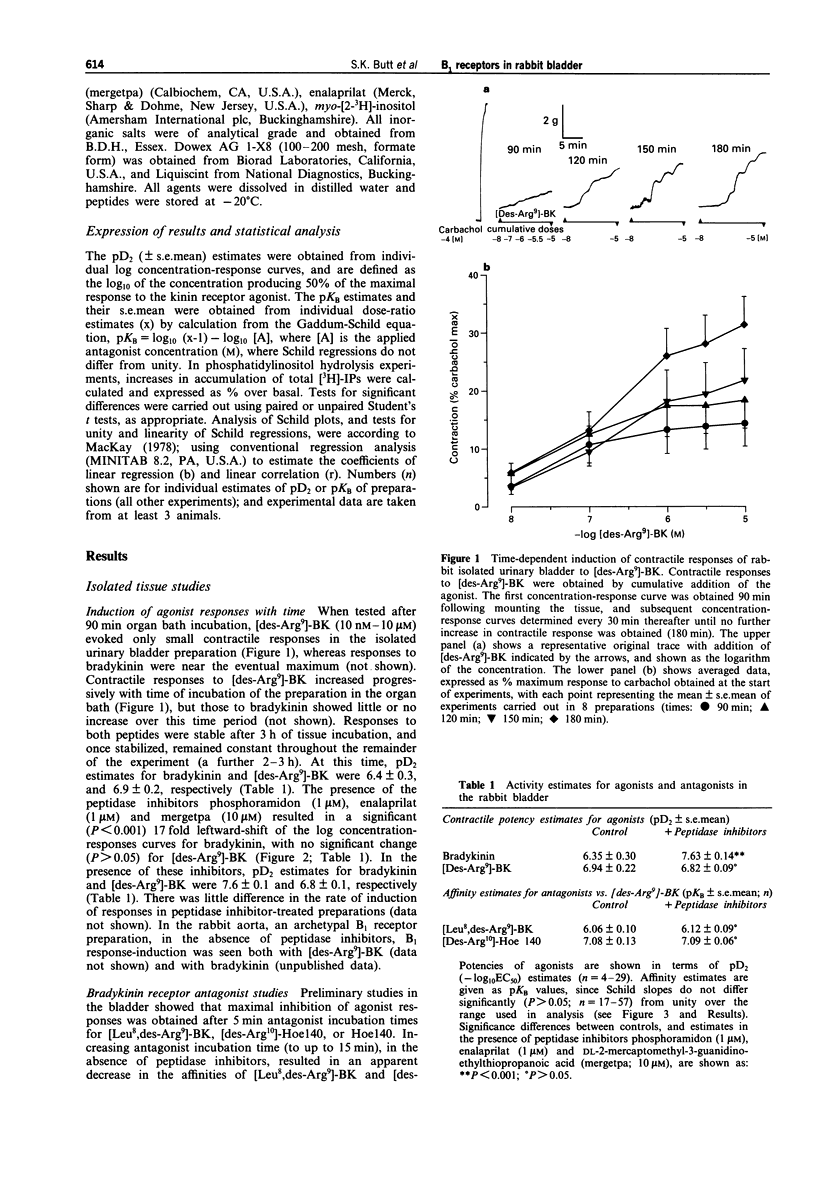
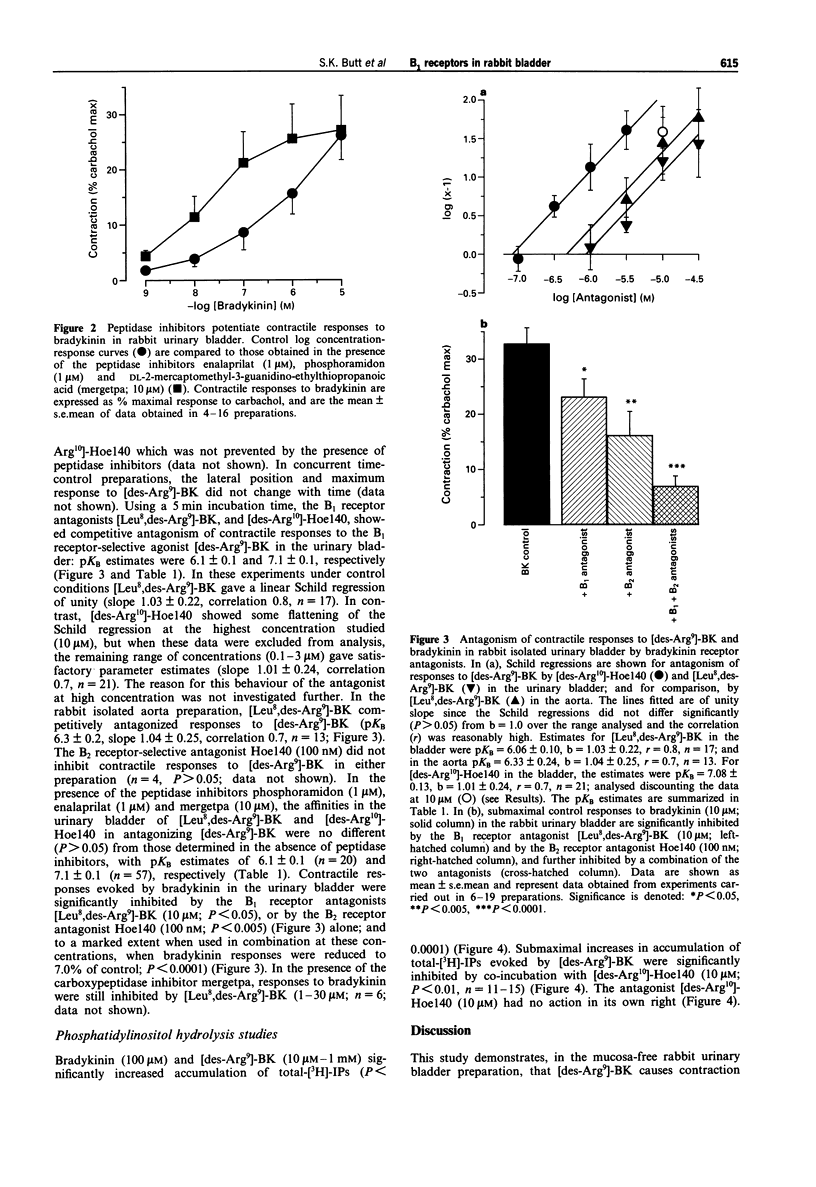
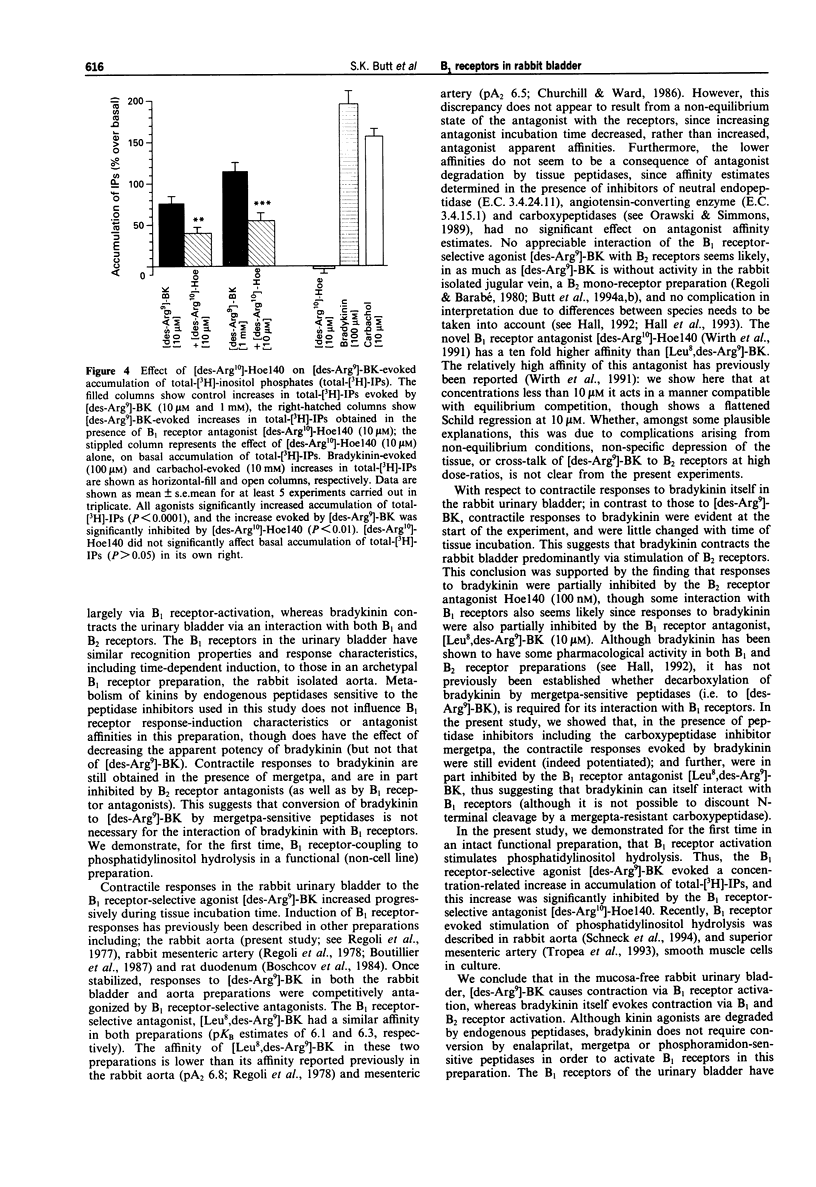
1. The aim of this study was to analyse the pharmacological characteristics, and second-messenger coupling-mechanisms, of bradykinin B1 receptors in an intact tissue, the rabbit urinary bladder; and to investigate the influence of inhibition of endogenous peptidases on kinin activities. 2. In preparations of rabbit mucosa-free urinary bladder, at 90 min after mounting of the preparations, bradykinin (1 nM-10 microM) evoked contractile responses. In contrast, the B1 receptor-selective agonist [des-Arg9]-BK (10 mM-10 microM) was only weakly active at this time. Contractile responses to [des-Arg9]-BK increased with time of tissue incubation in the organ bath, reaching a maximum after 3 h, when the pD2 estimates were 6.4 +/- 0.3 for bradykinin, and 6.9 +/- 0.2 for [des-Arg9]-BK. 3. Once stabilized, responses to [des-Arg9]-BK in the bladder were competitively antagonized by the B1 receptor-selective antagonists [Leu8,des-Arg9]-BK and D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Oic8,des-Arg9]-BK ([des-Arg10]-Hoe140) (pKB estimates were 6.1 +/- 0.1 and 7.1 +/- 0.1, respectively; n = 17-21), but responses were unaffected by the B2 receptor-selective antagonist D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Oic8]-BK (Hoe140) (100 nM; n = 4). Contractile responses to bradykinin itself were partially, but significantly, inhibited by the B1 receptor-selective antagonist, [Leu8,des-Arg9]-BK (10 microM) (P < 0.05), or by the B2 receptor-selective antagonist Hoe140 (100 nM) (P < 0.005) alone, and were largely blocked by a combination of the two antagonists (P < 0.0001).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschcov P., Paiva A. C., Paiva T. B., Shimuta S. I. Further evidence for the existence of two receptor sites for bradykinin responsible for the diphasic effect in the rat isolated duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthillier J., Deblois D., Marceau F. Studies on the induction of pharmacological responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;92(2):257–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow D. R., Curtis N. R., Suman-Chauhan N., Watling K. J., Williams B. J. Effects of tachykinins on inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in slices of hamster urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;90(1):211–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb16842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Farmer S. G., Steranka L. R. Bradykinin receptor antagonists. Med Res Rev. 1990 Apr-Jun;10(2):237–269. doi: 10.1002/med.2610100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill L., Ward P. E. Relaxation of isolated mesenteric arteries by des-Arg9-bradykinin stimulation of B1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 14;130(1-2):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Meeker S. A., Wilkins D. E. Evidence for a pulmonary B3 bradykinin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., DeSiato M. A. Effects of a novel nonpeptide bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist on intestinal and airway smooth muscle: further evidence for the tracheal B3 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;112(2):461–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J. L., Hall J. M., Morton I. K. Bradykinin receptors in the guinea-pig taenia caeci are similar to proposed BK3 receptors in the guinea-pig trachea, and are blocked by HOE 140. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):293–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M. Bradykinin receptors: pharmacological properties and biological roles. Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Nov;56(2):131–190. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90016-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Caulfield M. P., Watson S. P., Guard S. Receptor subtypes or species homologues: relevance to drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Oct;14(10):376–383. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Fox A. J., Morton I. K. Peptidase activity as a determinant of agonist potencies in some smooth muscle preparations. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 6;176(2):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90520-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque L., Drapeau G., Grose J. H., Rioux F., Marceau F. Vascular mode of action of kinin B1 receptors and development of a cellular model for the investigation of these receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1254–1262. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay D. How should values of pA2 and affinity constants for pharmacological competitive antagonists be estimated? J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 May;30(5):312–313. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orawski A. T., Simmons W. H. Degradation of bradykinin and its metabolites by rat brain synaptic membranes. Peptides. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Kelly D. Induction of bradykinin B1 receptors in vivo in a model of ultra-violet irradiation-induced thermal hyperalgesia in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1441–1444. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J., Park W. K. Receptors for bradykinin in rabbit aortae. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;55(4):855–867. doi: 10.1139/y77-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Marceau F., Barabé J. De novo formation of vascular receptors for bradykinin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;56(4):674–677. doi: 10.1139/y78-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneck K. A., Hess J. F., Stonesifer G. Y., Ransom R. W. Bradykinin B1 receptors in rabbit aorta smooth muscle cells in culture. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb 15;266(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropea M. M., Gummelt D., Herzig M. S., Leeb-Lundberg L. M. B1 and B2 kinin receptors on cultured rabbit superior mesenteric artery smooth muscle cells: receptor-specific stimulation of inositol phosphate formation and arachidonic acid release by des-Arg9-bradykinin and bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):930–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth K., Breipohl G., Stechl J., Knolle J., Henke S., Schölkens B. DesArg9-D-Arg[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Oic8]bradykinin (desArg10-[Hoe140]) is a potent bradykinin B1 receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 26;205(2):217–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90824-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


