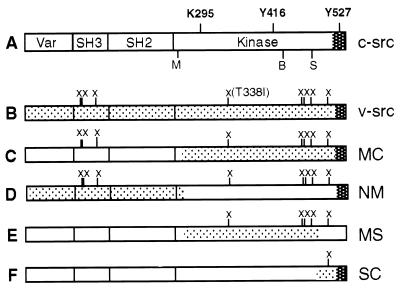
Figure 2.
src proteins used in this work. (A) Diagram of c-src, indicating the boundaries of the variable (Var), SH3, SH2, and kinase domains. Also shown are the location of the negative regulatory phosphorylation site (Y527), the major autophosphorylation site (Y416), and the conserved lysine in the ATP binding site (K295). M, B, and S, MluI, BglI, and SphI restriction sites, respectively, used to make v-src/c-src chimeras. (B) Diagram of v-src, indicating the amino acid changes (marked by X) and the C-terminal sequence (dark shading) that differ from c-src (see text). (C–F) v-src/c-src chimeras. Shaded portions represent sequences derived from v-src. The c-src/v-src chimeras are named according to the v-src restriction fragments they contain (e. g., MS is a chimera in which a MluI-SphI fragment of v-src is flanked by c-src sequences) (10).