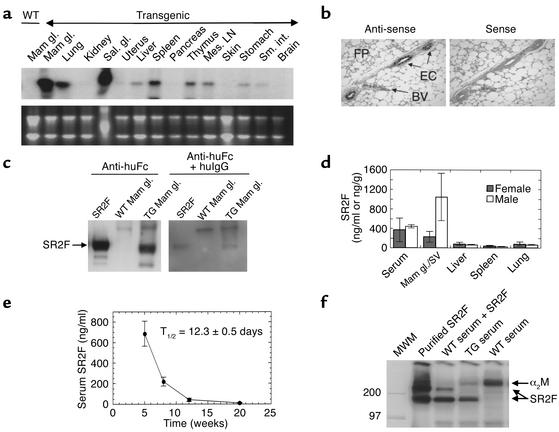
Figure 2.
TGF-β antagonist expression and function in the MMTV-SR2F mouse. (a) Expression of SR2F mRNA in different tissues. RNA was prepared from an adult virgin female transgenic mouse and probed for SR2F. (b) Cell type–specific expression of SR2F in the mammary gland. In situ hybridization showed specific expression of SR2F mRNA in the mammary ductal epithelial cells (ECs) but not in the mammary fat pad (FP) or blood vessels (BVs) of a virgin transgenic mouse. (c) SR2F protein in the transgenic mammary gland. Western blots of mammary gland extracts from wild-type or transgenic (TG) mice were probed with anti–human Fc antibody (anti-huFc), with or without an excess of human immunoglobulin G1 (huIgG) to demonstrate specificity. Purified SR2F was the positive control. (d) SR2F protein levels in serum and tissues from transgenic mice. Sera and tissue extracts from 2.5-month-old virgin transgenic mice were assayed for SR2F protein. Results are the mean ± SD for three mice of each sex. (e) In vivo stability of SR2F. Serum levels of SR2F in the wild-type offspring of hemizygous transgenic dams were determined various times after birth. The serum half-life (T1/2) of SR2F was calculated from the decay curve. (f) Ability of SR2F in transgenic serum to bind TGF-β1. Serum from wild-type or transgenic mice was probed for TGF-β binding proteins by ligand affinity crosslinking with 125I–TGF-β1. Purified SR2F spiked into saline or wild-type serum were the positive controls. Mam gl., mammary gland; Sal. Gl., salivary gland; Mes. LN, mesenteric lymph node ; Sal. gl, salivary gland; Sm. int., small intestine; SV, Seminal vesicle; MWM, molecular weight markers; α2M, α2-macroglobulin.