Abstract
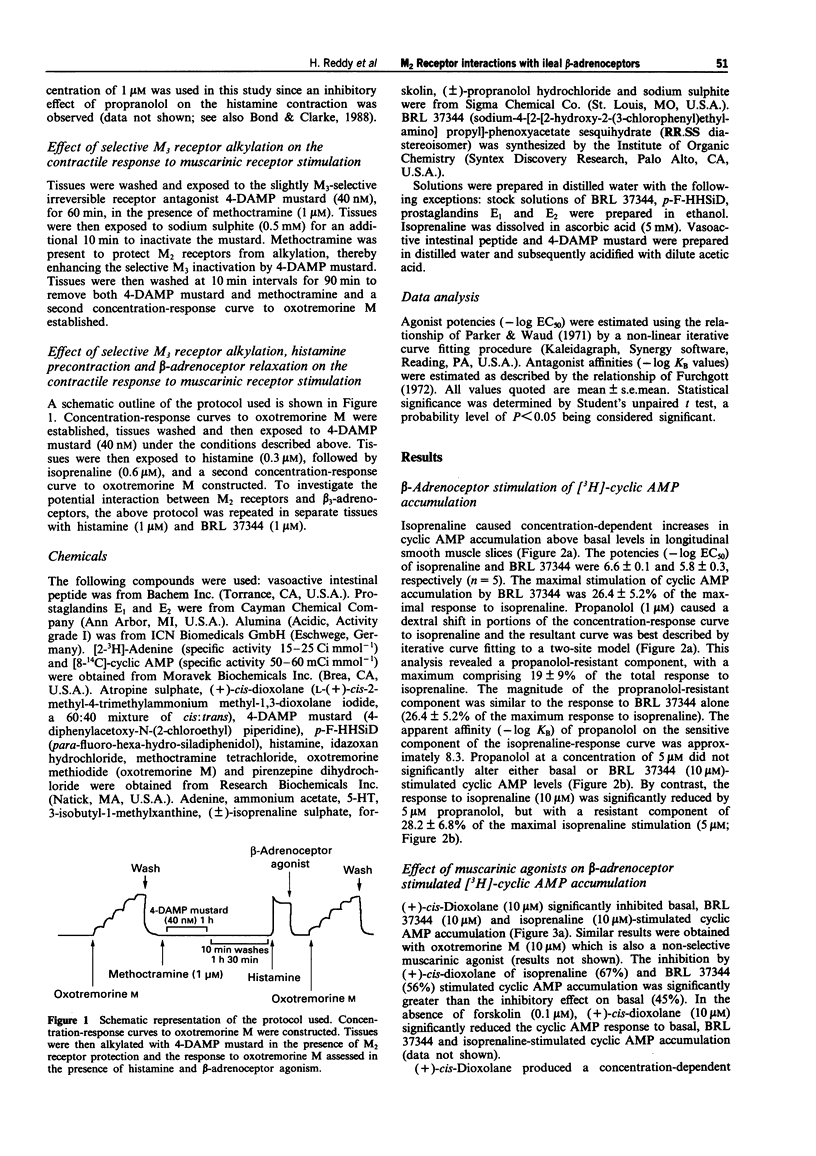
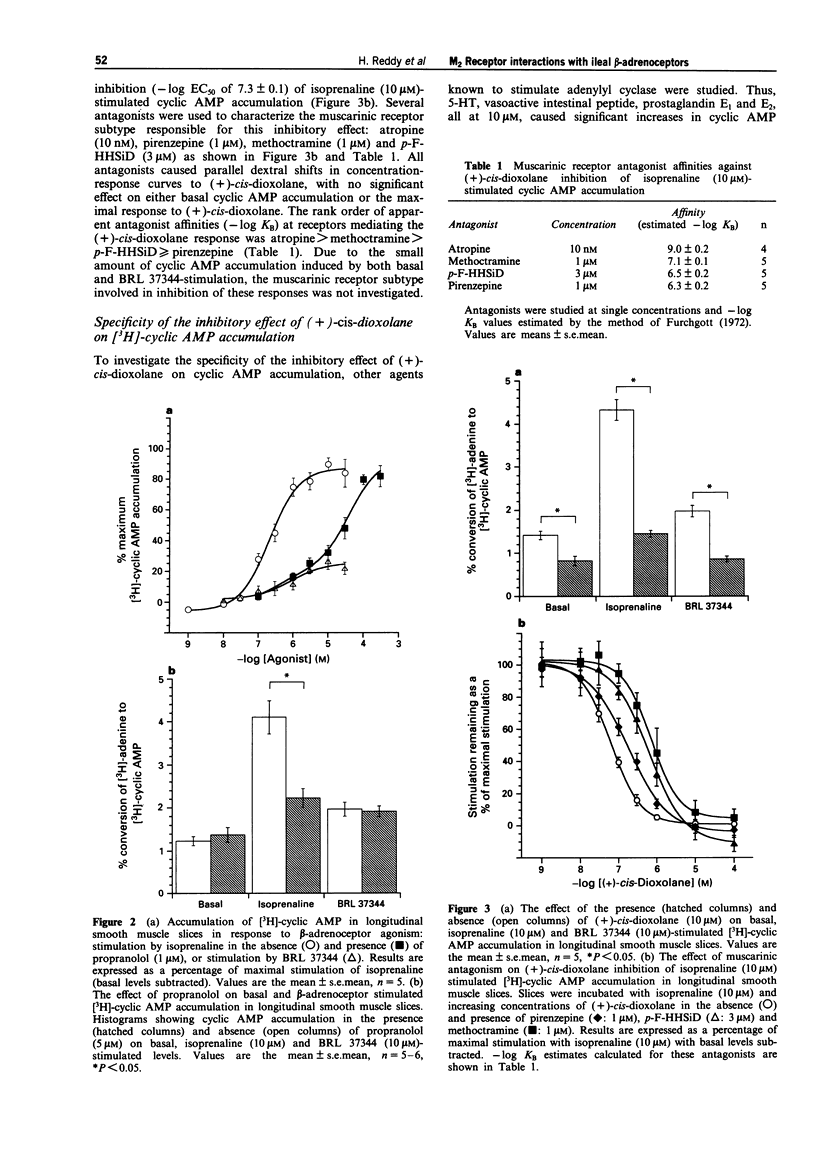
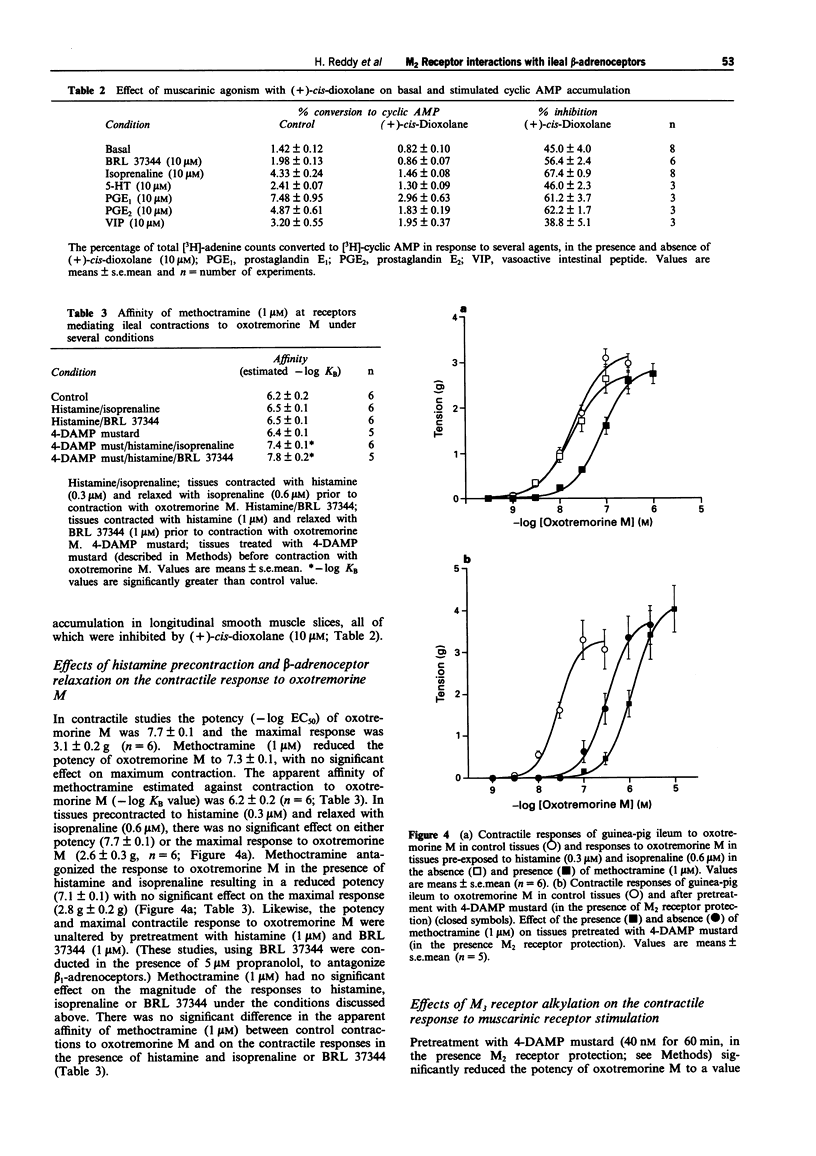
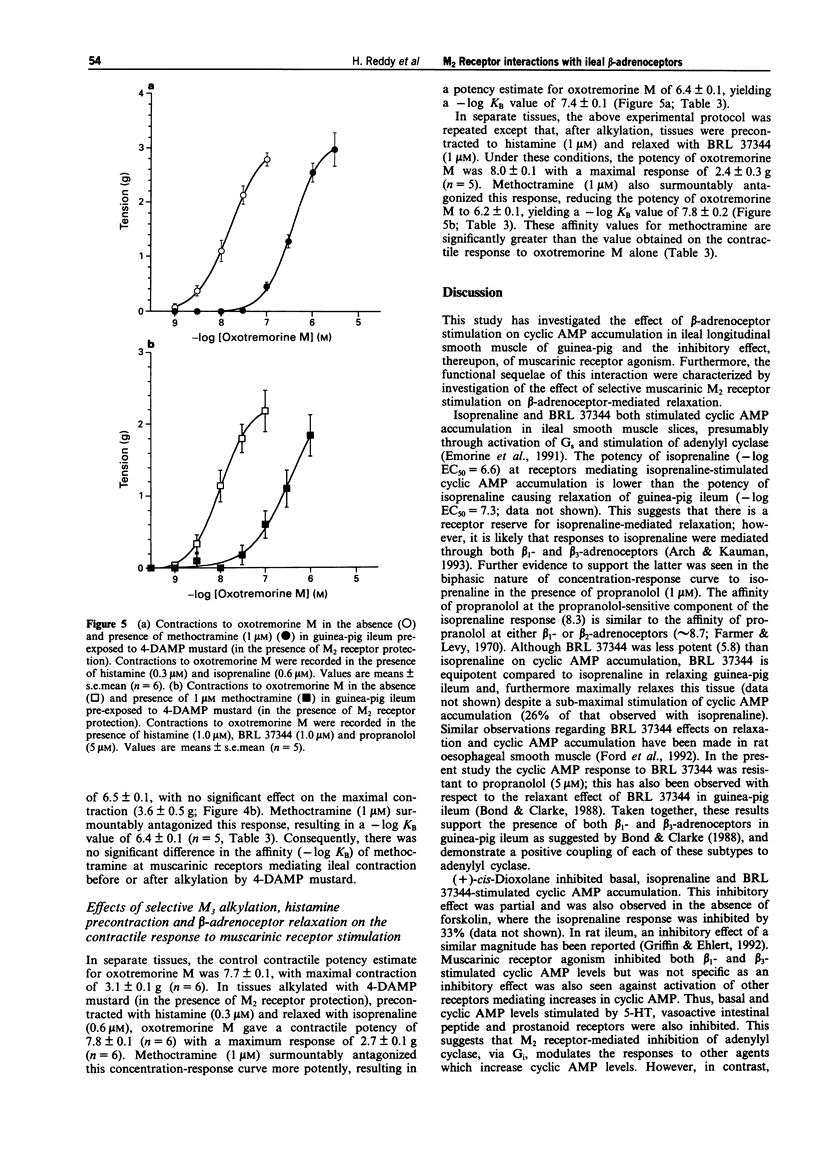
1. Contraction of guinea-pig ileum to muscarinic agonists is mediated by M3 receptors, even though they account for only 30% of the total muscarinic receptor population. The aim of this study was to characterize the biochemical and functional effects of stimulation of the predominant M2 muscarinic receptor (70%) and to investigate the hypothesis that M2 receptors specifically oppose beta-adrenoceptor-mediated effects in the ileum. 2. In guinea-pig ileal longitudinal smooth muscle slices, isoprenaline, a non-selective beta-adrenoceptor agonist, and BRL 37344 (sodium-4-[2-[2-hydroxy-2-(3- chlorophenyl)ethylamino]propyl]-phenoxyacetate sesquihydrate), a beta 3-adrenoceptor selective agonist, increased cyclic AMP accumulation with -log EC50 values of 6.6 +/- 0.1 and 5.8 +/- 0.1 respectively. Maximal stimulation by BRL 37344 (10 microM) was 26.4 +/- 5.2% of that observed with isoprenaline (10 microM). Isoprenaline (10 microM)-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation was significantly, but not completely, inhibited by propranolol (5 microM), with a propranolol-resistant component of 28.2 +/- 6.8% of the maximal stimulation to isoprenaline. In contrast, basal and BRL 37344 responses were resistant to this antagonist. These data provide evidence that both beta 1- and beta 3-adrenoceptors activate adenylyl cyclase in guinea-pig ileum. 3. Isoprenaline (10 microM)-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation was inhibited (67.4 +/- 0.9%) by the muscarinic agonist (+)-cis-dioxolane (-log EC50 = 7.3 +/- 0.1).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez R., Daniels D. V. A separation method for the assay of adenylylcyclase, intracellular cyclic AMP, and cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase using tritium-labeled substrates. Anal Biochem. 1992 May 15;203(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Ainsworth A. T., Cawthorne M. A., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Thody V. E., Wilson C., Wilson S. Atypical beta-adrenoceptor on brown adipocytes as target for anti-obesity drugs. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):163–165. doi: 10.1038/309163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Kaumann A. J. Beta 3 and atypical beta-adrenoceptors. Med Res Rev. 1993 Nov;13(6):663–729. doi: 10.1002/med.2610130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. The interaction of cyclic nucleotides and calcium in the control of cellular activity. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;6:1–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Clarke D. E. Agonist and antagonist characterization of a putative adrenoceptor with distinct pharmacological properties from the alpha- and beta-subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):723–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield M. P. Muscarinic receptors--characterization, coupling and function. Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Jun;58(3):319–379. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90027-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Adams D., Mistry R., Boyle J. P. Second messenger and ionic modulation of agonist-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover in airway smooth muscle. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Nov;21(4):1138–1145. doi: 10.1042/bst0211138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doods H. N., Willim K. D., Boddeke H. W., Entzeroth M. Characterization of muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig uterus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec 7;250(2):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90385-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterization of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors regulating cholinergic activity in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;64(2):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Harris G. C. Selective inactivation of muscarinic M2 and M3 receptors in guinea-pig ileum and atria in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):946–952. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Huff M. M., Montgomery W. W., Whiting R. L. Differential effects of pertussis toxin on muscarinic responses in isolated atria and smooth muscle. J Auton Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;8(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1988.tb00166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Michel A. D., Whiting R. L. Characterization of the muscarinic receptor subtype mediating contractions of the guinea-pig uterus. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;96(3):497–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Reddy H., Watson N., Challiss R. A. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in smooth muscle. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Apr;15(4):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Feve B., Pairault J., Briend-Sutren M. M., Marullo S., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg D. A. Structural basis for functional diversity of beta 1-, beta 2- and beta 3-adrenergic receptors. 1991 Mar 15-Apr 1Biochem Pharmacol. 41(6-7):853–859. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90188-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. B., Levy G. P. Differentiation of beta-adrenoreceptors by the use of blocking agents. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;22(2):145–146. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes L. B., Fryer A. D., Hirshman C. A. M2 muscarinic receptors inhibit isoproterenol-induced relaxation of canine airway smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):119–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo E., Monferini E., Ladinsky H., Hammer R. Muscarinic receptor heterogeneity in guinea pig intestinal smooth muscle: binding studies with AF-DX 116. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 23;141(3):475–477. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grana E., Lucchelli A., Zonta F., Santagostino-Barbone M. G., D'Agostino G. Comparative studies of the postjunctional activities of some very potent muscarinic agonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;332(3):213–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00504856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassby P. F., Broadley K. J. Characterization of beta-adrenoceptors mediating relaxation of the guinea-pig ileum. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;36(9):602–607. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. T., Ehlert F. J. Specific inhibition of isoproterenol-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation by M2 muscarinic receptors in rat intestinal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):221–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachur J. F., Sturm B. L., Gaginella T. S., Noronha-Blob L. Regulation of guinea pig ileal electrolyte transport by M3-muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in vitro. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;38(6):836–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchiorre C., Bolognesi M. L., Chiarini A., Minarini A., Spampinato S. Synthesis and biological activity of some methoctramine-related tetraamines bearing a 11-acetyl-5,11-dihydro-6H-pyrido[2,3-b][1,4]-benzodiazepin-6-one moiety as antimuscarinics: a second generation of highly selective M2 muscarinic receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1993 Nov 12;36(23):3734–3737. doi: 10.1021/jm00075a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian M. A., Malta E., Raper C. An homogeneous population of beta 1-adrenoceptors subserves inhibitory responses in guinea-pig ileal preparations. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;36(10):698–699. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micheletti R., Montagna E., Giachetti A. AF-DX 116, a cardioselective muscarinic antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):628–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. W., Koenig S. M., Popovich K. J., Kelly E., Tallet J., Leff A. R. Pertussis toxin augments beta-adrenergic relaxation of muscarinic contraction in canine trachealis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Feb;147(2):327–331. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.2.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. B., Waud D. R. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A. Differential inhibitory effect of isoproterenol on contractions of canine airways. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Sep;57(3):801–807. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.3.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares-da-Silva P., Fernandes M. H., Pinto-do-O P. C. Cell inward transport of L-DOPA and 3-O-methyl-L-DOPA in rat renal tubules. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;112(2):611–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. A., Baker S. A., Ehlert F. J. Functional role for the M2 muscarinic receptor in smooth muscle of guinea pig ileum. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):102–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. A., Hsu H. H., Griffin M. T., Hunter A. L., Luong T., Ehlert F. J. Conversion of N-(2-chloroethyl)-4-piperidinyl diphenylacetate (4-DAMP mustard) to an aziridinium ion and its interaction with muscarinic receptors in various tissues. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):718–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson N., Eglen R. M. Effects of muscarinic M2 and M3 receptor stimulation and antagonism on responses to isoprenaline of guinea-pig trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):179–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L. B., Buxton I. L. Muscarinic receptors in canine colonic circular smooth muscle. II. Signal transduction pathways. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):952–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


