Abstract
1. The pharmacological properties and location of H3 receptors modulating acetylcholine release have been investigated in non-superfused slices and synaptosomes of rat entorhinal cortex preloaded with [3H]-choline. 2. (R)alpha-methylhistamine, an H3-receptor agonist, potently inhibited the K(+)-evoked tritium release from slices, an effect antagonized by thioperamide, an H3-receptor antagonist, with nanomolar potency. 3. The K(+)-evoked tritium release from synaptosomes remained unaltered in the presence of the potent and selective H3-receptor agonists, imetit and (R)alpha-methylhistamine, suggesting that H3 receptors modulating acetylcholine release are not presynaptically located on cholinergic nerve terminals. 4. Phenylbutanoylhistamine and phenylpropylhistamine, two H3-receptor antagonists of moderate potency, failed to antagonize the inhibitory effects of (R)alpha-methylhistamine observed in slices. Unexpectedly, both compounds when used alone, inhibited tritium release from slices and synaptosomes with micromolar potency and to the same extent (by approximately 50% when added at a final concentration of 200 microM). This inhibitory effect did not involve H1, H2 or H3 receptors and was not mediated by an unknown histamine receptor site, since histamine used at a high concentration neither reproduced nor antagonized the effect of phenylbutanoylhistamine. It remained unaltered in the presence of scopolamine and was neither mimicked nor antagonized by vasoactive intestinal peptide, previously shown to be colocalized with acetylcholine in some neurones. 5. It is concluded that acetylcholine release in rat entorhinal cortex is modulated by H3 receptors presumably not located on cholinergic axon terminals.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
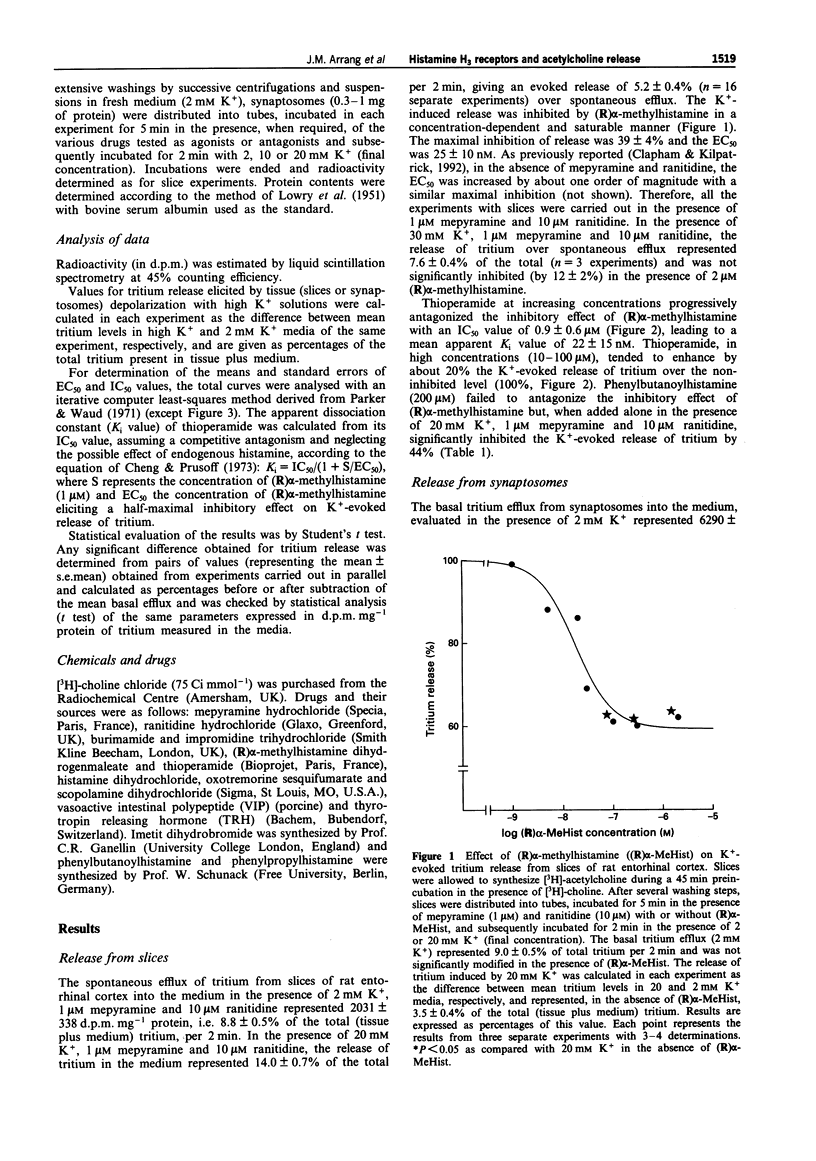
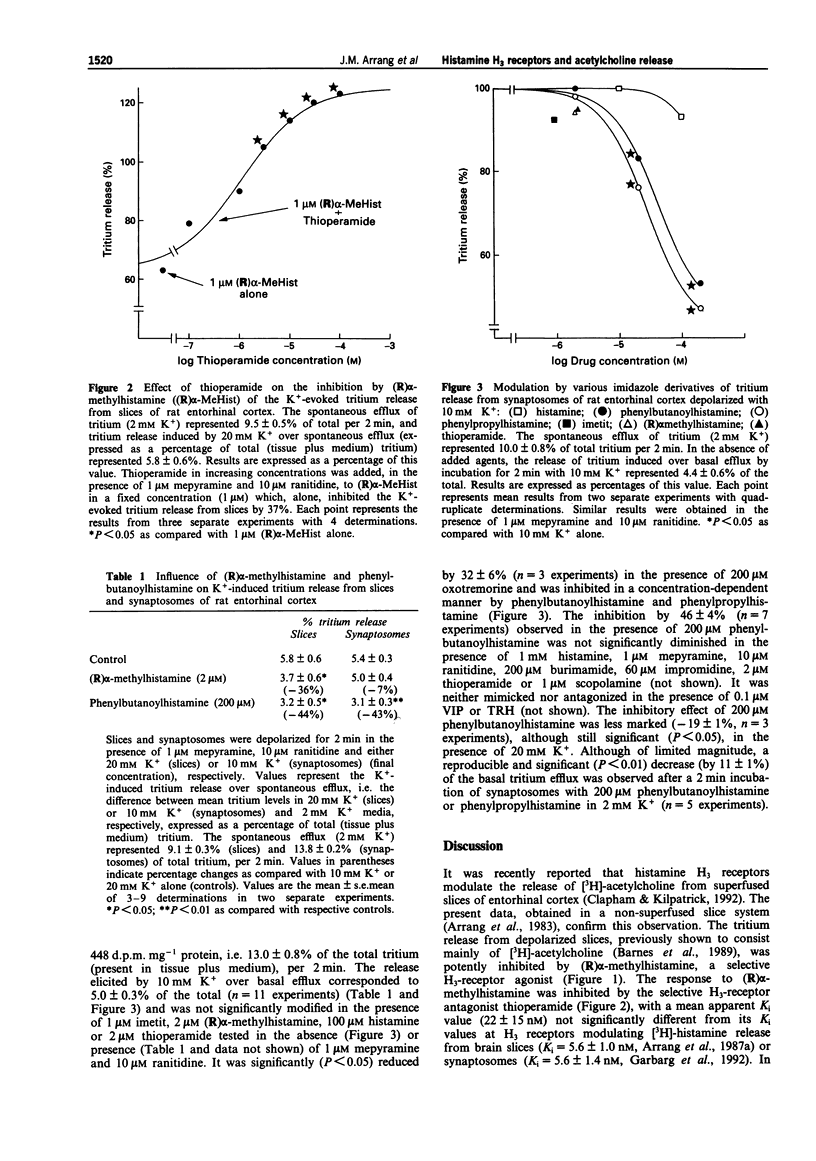


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Lancelot J. C., Lecomte J. M., Pollard H., Robba M., Schunack W., Schwartz J. C. Highly potent and selective ligands for histamine H3-receptors. Nature. 1987 May 14;327(6118):117–123. doi: 10.1038/327117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):832–837. doi: 10.1038/302832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Autoinhibition of histamine synthesis mediated by presynaptic H3-receptors. Neuroscience. 1987 Oct;23(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Autoregulation of histamine release in brain by presynaptic H3-receptors. Neuroscience. 1985 Jun;15(2):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Gulat-Marnay C., Defontaine N., Schwartz J. C. Regulation of histamine release in rat hypothalamus and hippocampus by presynaptic galanin receptors. Peptides. 1991 Sep-Oct;12(5):1113–1117. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(91)90067-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Roy J., Morgat J. L., Schunack W., Schwartz J. C. Histamine H3 receptor binding sites in rat brain membranes: modulations by guanine nucleotides and divalent cations. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr 25;188(4-5):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90005-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Barnes N. M., Costall B., Horovitz Z. P., Naylor R. J. Angiotensin II inhibits the release of [3H]acetylcholine from rat entorhinal cortex in vitro. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 3;491(1):136–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandina P., Knott P. J., Leung L. K., Green J. P. Stimulation of histamine H2 receptor in rat hypothalamus releases endogenous norepinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Apr;249(1):44–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham J., Kilpatrick G. J. Histamine H3 receptors modulate the release of [3H]-acetylcholine from slices of rat entorhinal cortex: evidence for the possible existence of H3 receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):919–923. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming P., Shaw C., Vincent S. R. High affinity histamine binding site is the H3 receptor: characterization and autoradiographic localization in rat brain. Synapse. 1991 Jun;8(2):144–151. doi: 10.1002/syn.890080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenstein F., Baughman R. W. Two types of cholinergic innervation in cortex, one co-localized with vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):153–155. doi: 10.1038/309153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Schlicker E., Neise A., Göthert M. Involvement of presynaptic H3 receptors in the inhibitory effect of histamine on serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;342(5):513–519. doi: 10.1007/BF00169038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarg M., Arrang J. M., Rouleau A., Ligneau X., Tuong M. D., Schwartz J. C., Ganellin C. R. S-[2-(4-imidazolyl)ethyl]isothiourea, a highly specific and potent histamine H3 receptor agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):304–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey J. A., del Prado M., Egan R. W., Kreutner W., Chapman R. W. Inhibition of sympathetic hypertensive responses in the guinea-pig by prejunctional histamine H3-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):347–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchi M., Raiteri M. On the presence in the cerebral cortex of muscarinic receptor subtypes which differ in neuronal localization, function and pharmacological properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Oct;235(1):230–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Mir M. I., Pollard H., Moreau J., Arrang J. M., Ruat M., Traiffort E., Schwartz J. C., Palacios J. M. Three histamine receptors (H1, H2 and H3) visualized in the brain of human and non-human primates. Brain Res. 1990 Sep 3;526(2):322–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91240-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T., Moskowitz M. A., Huang Z. UK-14,304, R(-)-alpha-methyl-histamine and SMS 201-995 block plasma protein leakage within dura mater by prejunctional mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 2;224(2-3):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90798-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki T., Okakura-Mochizuki K., Horii A., Yamamoto Y., Yamatodani A. Histaminergic modulation of hippocampal acetylcholine release in vivo. J Neurochem. 1994 Jun;62(6):2275–2282. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62062275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. B., Waud D. R. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H., Moreau J., Arrang J. M., Schwartz J. C. A detailed autoradiographic mapping of histamine H3 receptors in rat brain areas. Neuroscience. 1993 Jan;52(1):169–189. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90191-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Leardi R., Marchi M. Heterogeneity of presynaptic muscarinic receptors regulating neurotransmitter release in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Behling A., Lümmen G., Göthert M. Histamine H3A receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in the mouse brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;345(4):489–493. doi: 10.1007/BF00176630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Fink K., Detzner M., Göthert M. Histamine inhibits dopamine release in the mouse striatum via presynaptic H3 receptors. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1993;93(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01244933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Fink K., Hinterthaner M., Göthert M. Inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rat brain cortex via presynaptic H3 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6):633–638. doi: 10.1007/BF00717738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Kilpatrick G. J. Characterization of histamine-H3 receptors controlling non-adrenergic non-cholinergic contractions of the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):667–674. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Zweig A., Granzow R. T., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W. Biexponential kinetics of (R)-alpha-[3H]methylhistamine binding to the rat brain H3 histamine receptor. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1612–1616. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Zweig A., Shih N. Y., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Identification of two H3-histamine receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):610–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. Some properties of synaptic membranes isolated from the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):982–998. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


