Abstract
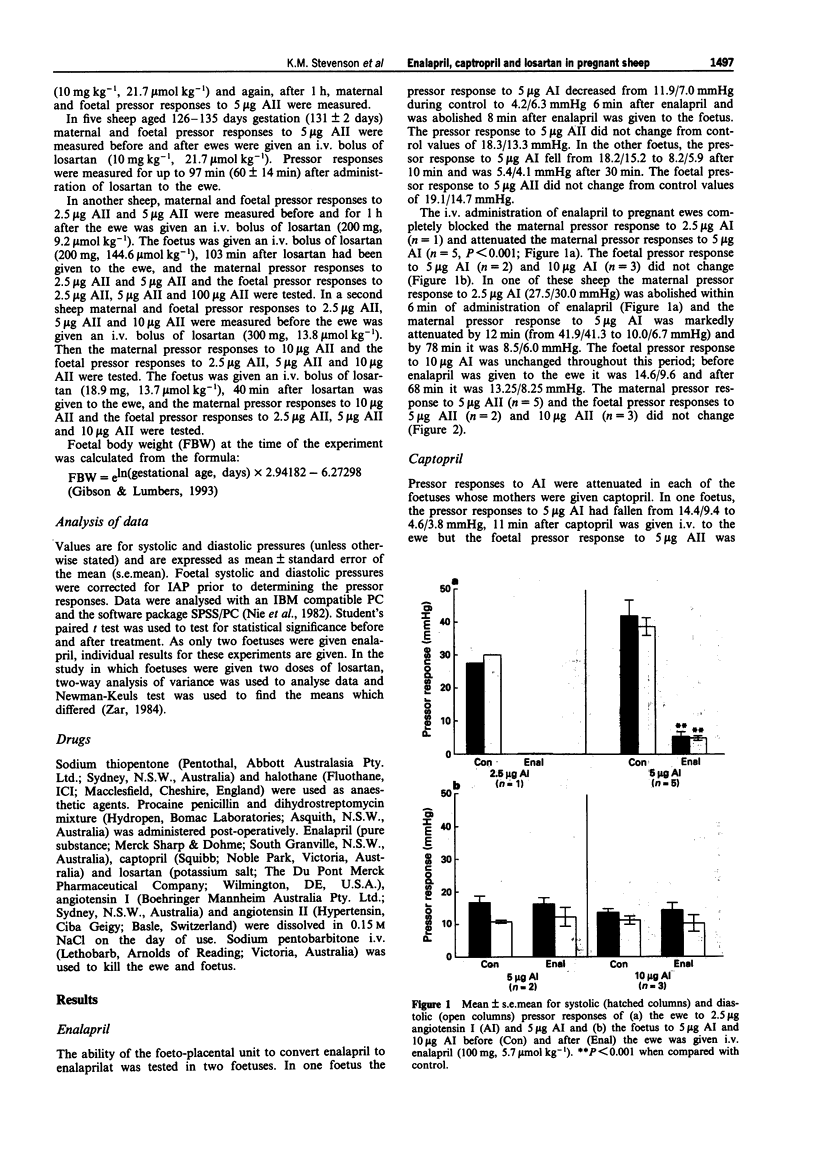
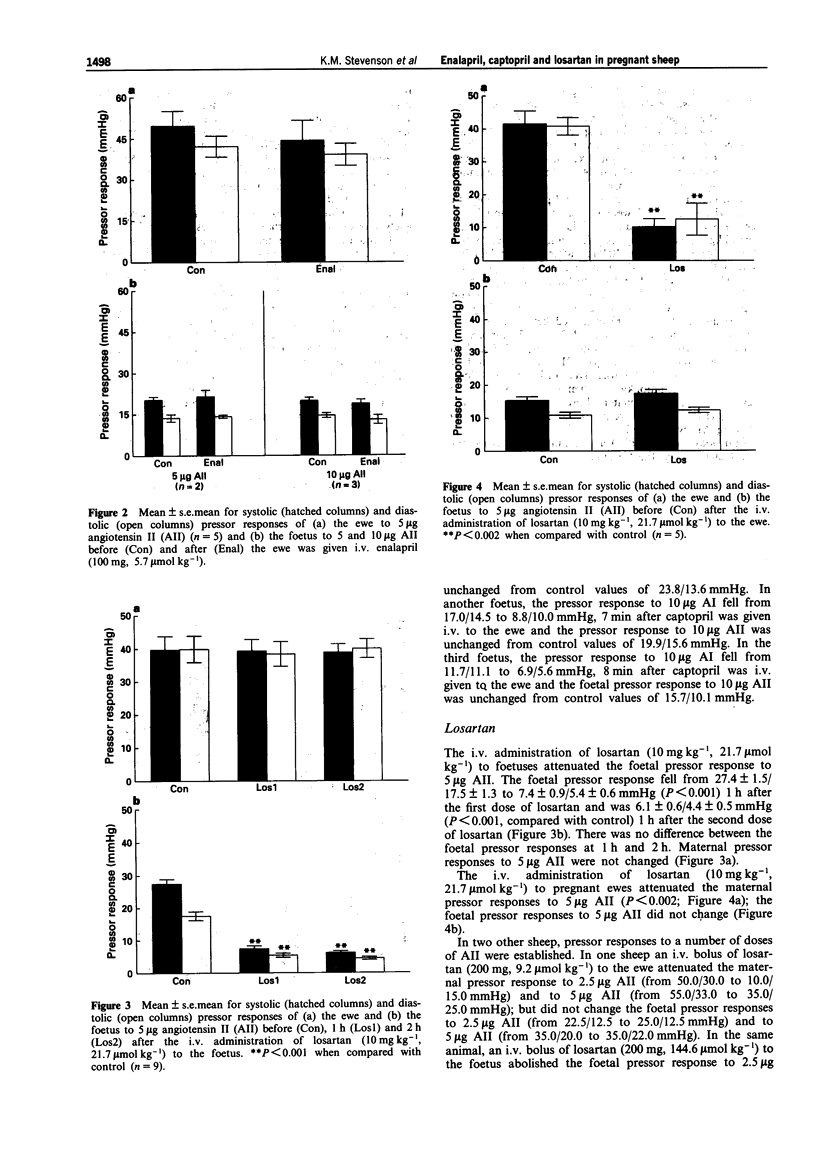
1. The transplacental transfers of three drugs (enalapril, captopril and losartan) which block the renin angiotensin system and have different lipophilicities were studied in chronically catheterized foetal sheep (125-139 days gestation). 2. The ability of the foeto-placental unit to convert enalapril to enalaprilat was studied in two chronically catheterized foetuses. Enalapril (3 mg kg-1, 7.9 mumol kg-1) given i.v. to the foetuses abolished the foetal pressor response to 5 micrograms angiotensin I (AI) in one foetus and attenuated the pressor response in the other. 3. Enalapril (100 mg, 5.7 mumol kg-1) given i.v. to the ewe (n = 5) abolished the maternal pressor response to 2.5 micrograms AI (n = 1) and attenuated the maternal pressor response to 5 micrograms AI (n = 5, P < 0.001). The foetal pressor response to 5 micrograms AI (n = 2) and 10 micrograms AI (n = 3) did not change. The maternal and foetal pressor responses to angiotensin II (AII; n = 5) did not change. 4. Foetal pressor responses to 5 micrograms AI (n = 1) and 10 micrograms AI (n = 2) were attenuated within 11 min of their mothers (n = 3) being given i.v. captopril (15 mg, 1.5 mumol kg-1). Foetal pressor responses to 5 micrograms AII (n = 1) and to 10 micrograms AII (n = 2) did not change. 5. Losartan (100 mg, kg-1, 21.7 mumol kg-1) given i.v. to the foetus (n = 9) attenuated the foetal pressor response to 5 micrograms AII (P < 0.001) but the maternal pressor response to 5 micrograms AII did not change.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biollaz J., Burnier M., Turini G. A., Brunner D. B., Porchet M., Gomez H. J., Jones K. H., Ferber F., Abrams W. B., Gavras H. Three new long-acting converting-enzyme inhibitors: relationship between plasma converting-enzyme activity and response to angiotensin I. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 May;29(5):665–670. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton Pipkin F., Symonds E. M., Turner S. R. The effect of captopril (SQ14,225) upon mother and fetus in the chronically cannulated ewe and in the pregnant rabbit. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:415–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton Pipkin F., Wallace C. P. The effect of enalapril (MK421), an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, on the conscious pregnant ewe and her foetus. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;87(3):533–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10195.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Wang F. L., Fung W. C., Harvey C. M., DeForrest J. M. Differentiation of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors by their selective inhibition of ACE in physiologically important target organs. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Apr;2(4):294–306. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.4.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Soffer R. L. Pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme. Structural and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6762–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavras H., Biollaz J., Waeber B., Brunner H. R., Gavras I., Davies R. O. Antihypertensive effect of the new oral angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor "MK-421". Lancet. 1981 Sep 12;2(8246):543–547. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90937-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson K. J., Lumbers E. R. The roles of arginine vasopressin in fetal sodium balance and as a mediator of the effects of fetal "stress". J Dev Physiol. 1993 Mar;19(3):125–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady E. F., Sechi L. A., Griffin C. A., Schambelan M., Kalinyak J. E. Expression of AT2 receptors in the developing rat fetus. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):921–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI115395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. M., Sweet C. S., Ulm E. H., Backlund E. P., Morris A. A., Weitz D., Bohn D. L., Wenger H. C., Vassil T. C., Stone C. A. Effect of N-[(S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-L-Ala-L-Pro and its ethyl ester (MK-421) on angiotensin converting enzyme in vitro and angiotensin I pressor responses in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):552–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröne H. J., Simon M., Fuchs E. Autoradiographic characterization of angiotensin receptor subtypes in fetal and adult human kidney. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):F326–F331. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.2.F326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M., Amidon G. L. Passive and carrier-mediated intestinal absorption components of captopril. J Pharm Sci. 1988 Dec;77(12):1007–1011. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600771204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott P. D., Thorpe S. S., Lamont C. A. Congenital renal dysgenesis possibly due to captopril. Lancet. 1989 Feb 25;1(8635):451–451. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo S. H., Cody R. J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. A review. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1985 Sep-Oct;10(5):377–391. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198510050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. H., Chen I. W., Ulm E. H., Duggan D. E. Differential renal handling of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors enalaprilat and lisinopril in rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 1988 May-Jun;16(3):392–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbers E. R., Burrell J. H., Menzies R. I., Stevens A. D. The effects of a converting enzyme inhibitor (captopril) and angiotensin II on fetal renal function. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):821–827. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbers E. R., Kingsford N. M., Menzies R. I., Stevens A. D. Acute effects of captopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, on the pregnant ewe and fetus. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 2):R754–R760. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.262.5.R754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbers E. R., Stevens A. D. The effects of frusemide, saralasin and hypotension on fetal plasma renin activity and on fetal renal function. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:479–490. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., Lonigro A. J. Release of a prostaglandin E-like substance from canine kidney by bradykinin. Circ Res. 1972 Jul;31(1):36–43. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkin B. L. Maternal and fetal distribution of drugs in pregnancy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Jul-Aug;14(4):643–647. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973144part2643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. J., Crantz F. R., Hollenberg N. K., Koletsky R. J., Leboff M. S., Swartz S. L., Levine L., Podolsky S., Dluhy R. G., Williams G. H. Contribution of prostaglandins to the antihypertensive action of captopril in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):168–173. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtawa M., Takayama F., Saitoh K., Yoshinaga T., Nakashima M. Pharmacokinetics and biochemical efficacy after single and multiple oral administration of losartan, an orally active nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist, in humans. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;35(3):290–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1993.tb05696.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Rubin B., Cushman D. W. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):441–444. doi: 10.1126/science.191908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranadive S. A., Chen A. X., Serajuddin A. T. Relative lipophilicities and structural-pharmacological considerations of various angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Pharm Res. 1992 Nov;9(11):1480–1486. doi: 10.1023/a:1015823315983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg A. D., Lorenz R. Can captopril cause fetal and neonatal renal failure? Pediatr Pharmacol (New York) 1984;4(3):189–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubiger G., Flury G., Nussberger J. Enalapril for pregnancy-induced hypertension: acute renal failure in a neonate. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Feb;108(2):215–216. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Chiu A. T., Wong P. C., Herblin W. F., Timmermans P. B. Pharmacology of nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:135–165. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz S. L., Williams G. H., Hollenberg N. K., Levine L., Dluhy R. G., Moore T. J. Captopril-induced changes in prostaglandin production: relationship to vascular responses in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1257–1264. doi: 10.1172/JCI109788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz S. L., Williams G. H., Hollenberg N. K., Moore T. J., Dluhy R. G. Converting enzyme inhibition in essential hypertension: the hypotensive response does not reflect only reduced angiotensin II formation. Hypertension. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):106–111. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.1.2.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet C. S., Gross D. M., Arbegast P. T., Gaul S. L., Britt P. M., Ludden C. T., Weitz D., Stone C. A. Antihypertensive activity of N-[(S)-1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]-L-Ala-L-Pro (MK-421), an orally active converting enzyme inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):558–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Strömberg C., Viswanathan M., Saavedra J. M. Angiotensin-II receptor subtypes in fetal tissue of the rat: autoradiography, guanine nucleotide sensitivity, and association with phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):1075–1082. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Viswanathan M., Strömberg C., Saavedra J. M. Type-1 and type-2 angiotensin II receptors in fetal rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 May 30;198(1):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90566-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulm E. H. Enalapril maleate (MK-421), a potent, nonsulfhydryl angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor: absorption, disposition, and metabolism in man. Drug Metab Rev. 1983;14(1):99–110. doi: 10.3109/03602538308991383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan M., Tsutsumi K., Correa F. M., Saavedra J. M. Changes in expression of angiotensin receptor subtypes in the rat aorta during development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1361–1367. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91723-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Rudolph A. M., Benet L. Z. Pharmacokinetics of drugs and metabolites in the maternal-placental-fetal unit: general principles. NIDA Res Monogr. 1985;60:25–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Hart S. D., Duncia J. V., Timmermans P. B. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Studies with DuP 753 and EXP3174 in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 24;202(3):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90274-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Price W. A., Chiu A. T., Duncia J. V., Carini D. J., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L., Timmermans P. B. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. IX. Antihypertensive activity in rats of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):726–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Price W. A., Chiu A. T., Duncia J. V., Carini D. J., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L., Timmermans P. B. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. VIII. Characterization of functional antagonism displayed by DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):719–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Price W. A., Jr, Chiu A. T., Duncia J. V., Carini D. J., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L., Timmermans P. B. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. XI. Pharmacology of EXP3174: an active metabolite of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G., Levin Y. A dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase that converts angiotensin I and inactivates bradykinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 21;214(2):374–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G., Levin Y. Characterization of a dipeptide hydrolase (kininase II: angiotensin I converting enzyme). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


