Abstract
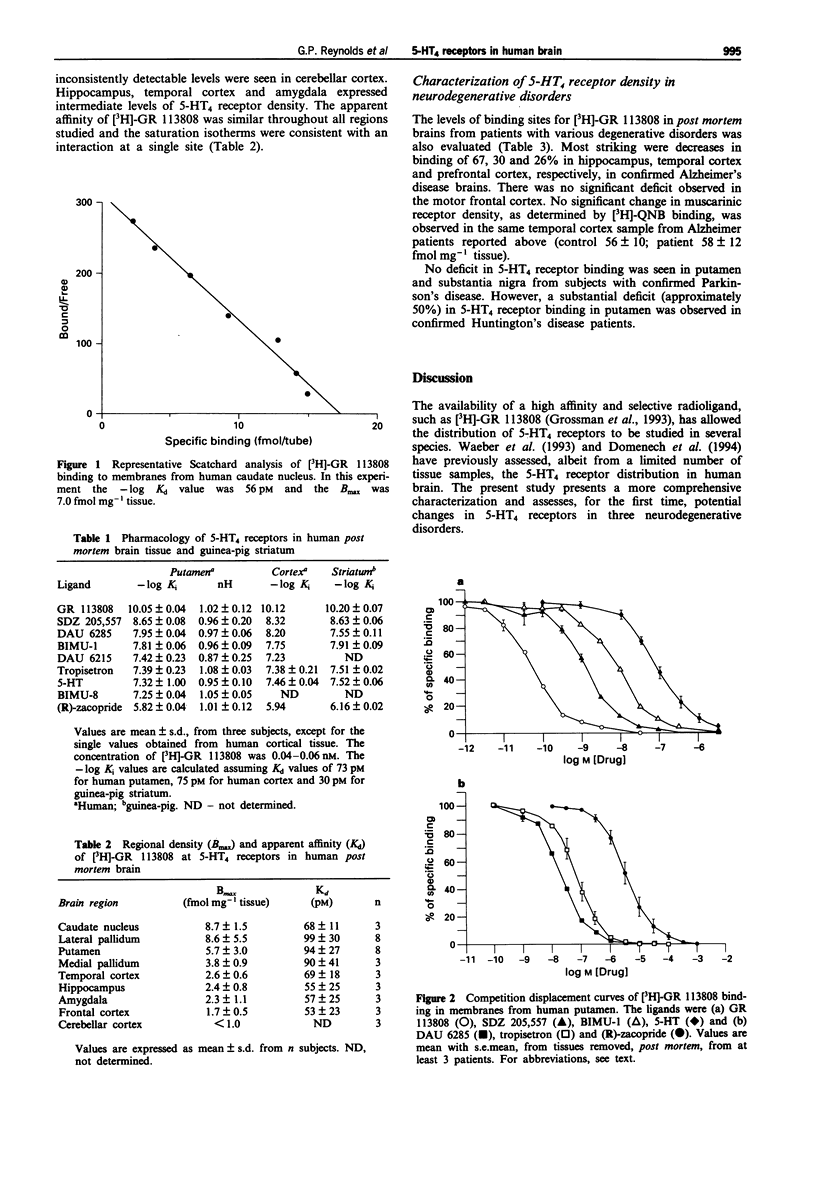
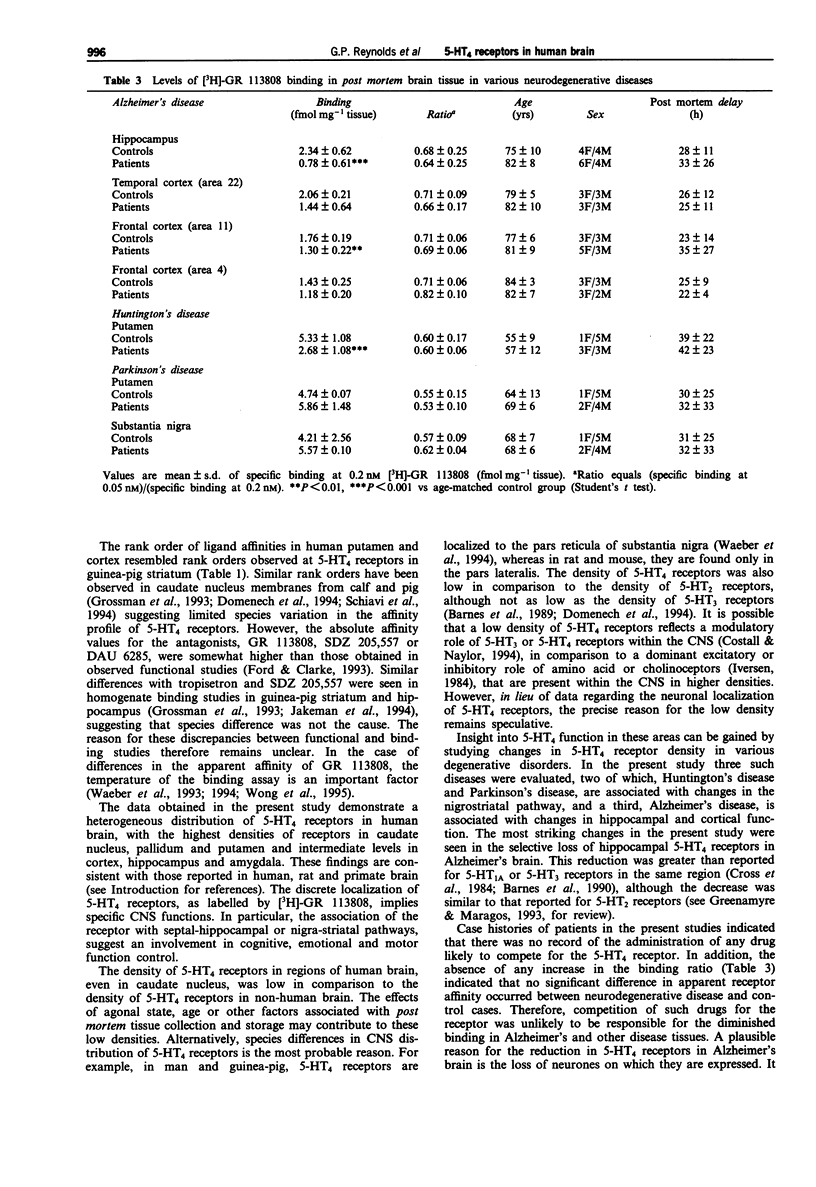
1. The distribution, pharmacology and effects of neurodegenerative diseases on 5-HT4 receptors in human brain have been characterized in vitro. 2. The 5-HT4 receptor in post mortem human brain tissue was specifically labelled with [3H]-GR 113808. In human putamen, this ligand labelled a homogeneous population of sites, with an apparent affinity (-log Kd) of 10.1 and a density (Bmax) of 5.73 fmol mg-1 tissue. The pharmacology of this site was characterized by use of a series of displacing ligands, and the following rank order of apparent affinities (with mean +/- s.d. -log Ki values in parentheses) was generated: GR113808 (10.05 +/- 0.04) > SDZ 205,557 (8.65 +/- 0.08) > DAU 6285 (7.95 +/- 0.04) > BIMU-1 (7.81 +/- 0.06) > DAU 6215 (7.42 +/- 0.23) > tropisetron (7.39 +/- 0.23) > 5-HT (7.32 +/- 1.00) > BIMU-8 (7.25 +/- 0.04) > (R)-zacopride (5.82 +/- 0.04). The Hill coefficients were not significantly different from unity, consistent with an interaction at a single site. A comparison of the affinities of these compounds with those obtained from guinea-pig striatum indicated no evidence of species differences. 3. The regional distribution of 5-HT4 receptors was assessed by determining the density of binding sites for [3H]-GR 113808.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade R., Chaput Y. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4-like receptors mediate the slow excitatory response to serotonin in the rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):930–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Barnes N. M., Costall B., Ironside J. W., Naylor R. J. Identification and characterisation of 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 recognition sites in human brain tissue. J Neurochem. 1989 Dec;53(6):1787–1793. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes N. M., Costall B., Naylor R. J., Williams T. J., Wischik C. M. Normal densities of 5-HT3 receptor recognition sites in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport. 1990 Nov-Dec;1(3-4):253–254. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199011000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costall B., Naylor R. J. The pharmacology of the 5-HT4 receptor. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1993 Nov;8 (Suppl 2):11–18. doi: 10.1097/00004850-199311002-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. J., Crow T. J., Ferrier I. N., Johnson J. A., Bloom S. R., Corsellis J. A. Serotonin receptor changes in dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neurochem. 1984 Dec;43(6):1574–1581. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doménech T., Beleta J., Fernández A. G., Gristwood R. W., Cruz Sánchez F., Tolosa E., Palacios J. M. Identification and characterization of serotonin 5-HT4 receptor binding sites in human brain: comparison with other mammalian species. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Jan;21(1-2):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Bouhelal R., Sebben M., Cory R., Bockaert J. A nonclassical 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor positively coupled with adenylate cyclase in the central nervous system. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):880–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Bockaert J. The gastrointestinal prokinetic benzamide derivatives are agonists at the non-classical 5-HT receptor (5-HT4) positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;340(4):403–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00167041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Bley K., Bonhaus D. W., Clark R. D., Hegde S. S., Johnson L. G., Leung E., Wong E. H. RS 23597-190: a potent and selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn D. L., Zabrowski D. L., Becker D. P., Nosal R., Villamil C. I., Gullikson G. W., Moummi C., Yang D. C. SC-53116: the first selective agonist at the newly identified serotonin 5-HT4 receptor subtype. J Med Chem. 1992 Apr 17;35(8):1486–1489. doi: 10.1021/jm00086a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Baxter G. S., Eglen R. M., Clarke D. E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates cyclic AMP formation in the tunica muscularis mucosae of the rat oesophagus via 5-HT4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 28;211(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Clarke D. E. The 5-HT4 receptor. Med Res Rev. 1993 Nov;13(6):633–662. doi: 10.1002/med.2610130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forno L. S. Neuropathologic features of Parkinson's, Huntington's, and Alzheimer's diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 May 11;648:6–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb24519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis J., Burnham W. M. [3H]Phenytoin identifies a novel anticonvulsant-binding domain on voltage-dependent sodium channels. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;42(6):1097–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey U., Huang Y. Y., Kandel E. R. Effects of cAMP simulate a late stage of LTP in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.8389057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Maragos W. F. Neurotransmitter receptors in Alzheimer disease. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1993 Summer;5(2):61–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman C. J., Kilpatrick G. J., Bunce K. T. Development of a radioligand binding assay for 5-HT4 receptors in guinea-pig and rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):618–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes R. A., Miller K., Akira S., Lin Y. C., Friedman C. I., Kim M. H. Pregnancy can be established in superovulated adult rats treated with progesterone and an aromatase inhibitor. Life Sci. 1993;52(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90289-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. The Ferrier Lecture, 1983. Amino acids and peptides: fast and slow chemical signals in the nervous system? Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 May 22;221(1224):245–260. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakeman L. B., To Z. P., Eglen R. M., Wong E. H., Bonhaus D. W. Quantitative autoradiography of 5-HT4 receptors in brains of three species using two structurally distinct radioligands, [3H]GR113808 and [3H]BIMU-1. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Aug;33(8):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90162-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R. Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative disorder. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):581–590. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg A., Larsson C., Adolfsson R., Alafuzoff I., Winblad B. Muscarinic receptor compensation in hippocampus of Alzheimer patients. J Neural Transm. 1983;56(1):13–19. doi: 10.1007/BF01243370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. P., Pearson S. J., Heathfield K. W. Dementia in Huntington's disease is associated with neurochemical deficits in the caudate nucleus, not the cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1990 May 18;113(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90501-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavi G. B., Brunet S., Rizzi C. A., Ladinsky H. Identification of serotonin 5-HT4 recognition sites in the porcine caudate nucleus by radioligand binding. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber C., Sebben M., Grossman C., Javoy-Agid F., Bockaert J., Dumuis A. [3H]-GR113808 labels 5-HT4 receptors in the human and guinea-pig brain. Neuroreport. 1993 Sep 10;4(11):1239–1242. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199309000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber C., Sebben M., Nieoullon A., Bockaert J., Dumuis A. Regional distribution and ontogeny of 5-HT4 binding sites in rodent brain. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):527–541. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


