Abstract
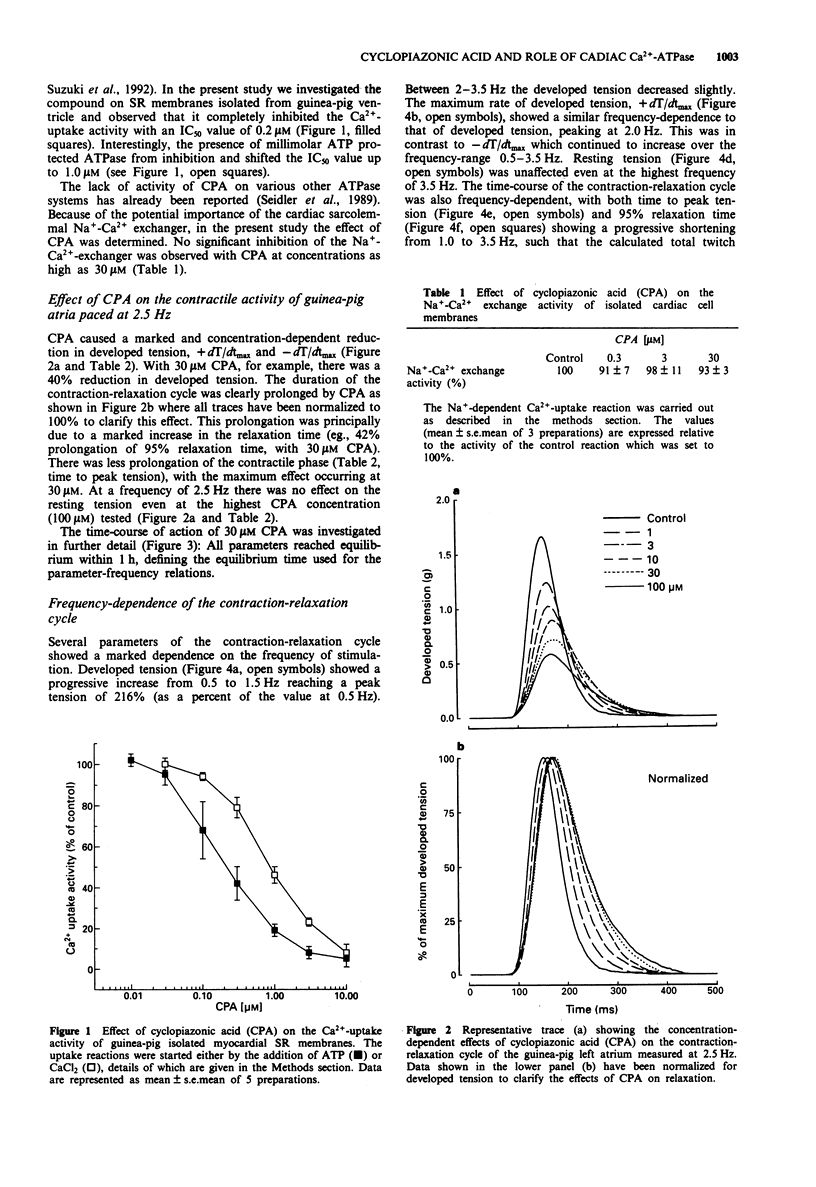
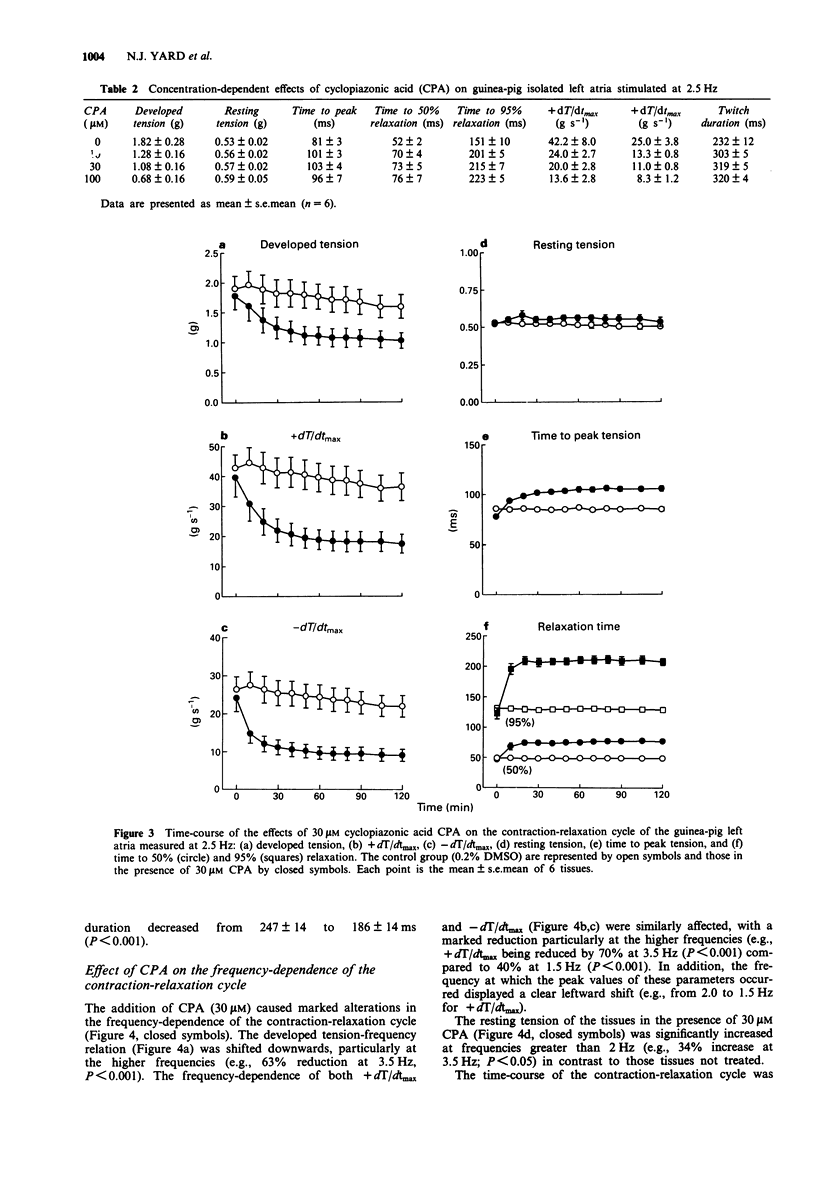
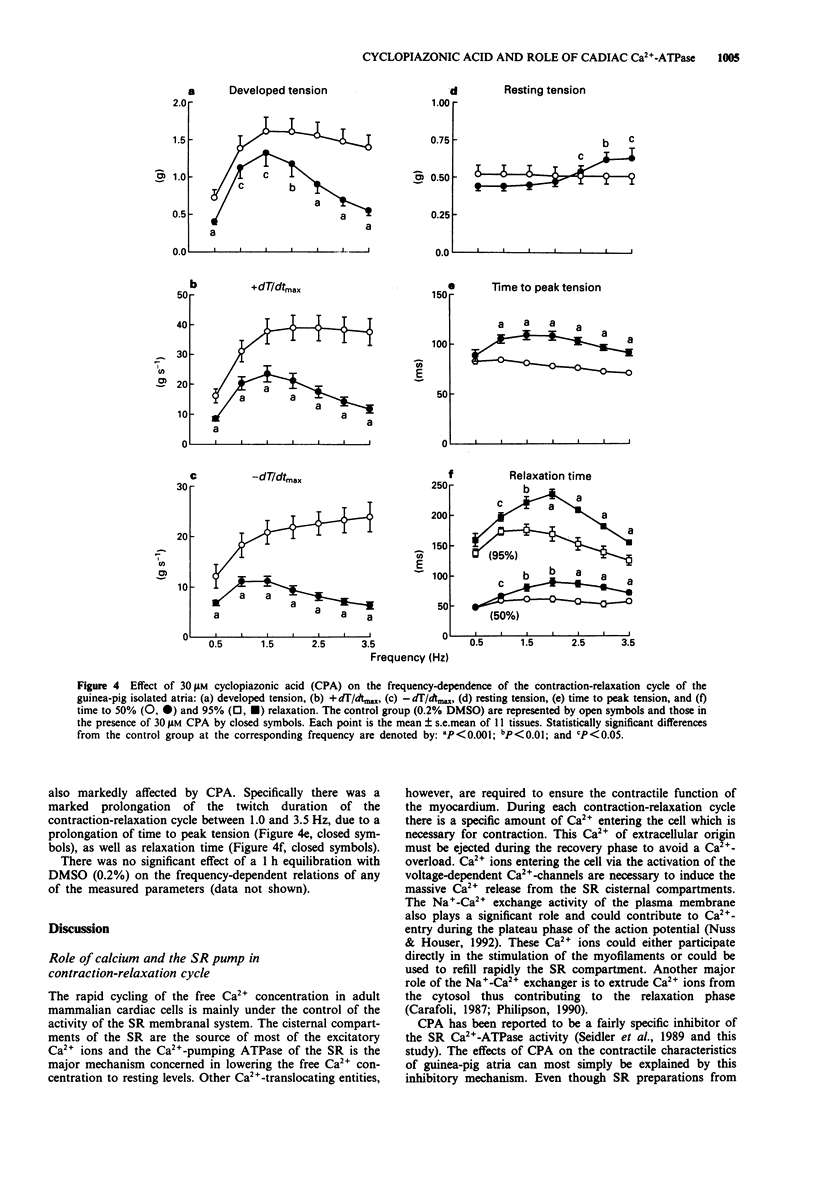
1. The relevance of a functional sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) membrane system to the contraction-relaxation cycle and to the force-frequency relationship of guinea-pig atrial tissue was investigated. Cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) was used to inhibit selectively the activity of the SR Ca(2+)-ATPase. IC50 values of 0.2 microM or 1.0 microM were measured in guinea-pig isolated SR membranes in the absence or presence of millimolar ATP, respectively. CPA (0.3-30 microM) did not inhibit the activity of the sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca(2+)-exchanger as measured in isolated cardiac cell membrane preparations. 2. In guinea-pig isolated left atrium paced at 2.5 Hz (30 degrees C), CPA (1-100 microM) produced a concentration-dependent reduction in developed tension and a fall in the maximum rate of tension increase (+dT/dtmax) and decrease (-dT/dtmax). The twitch duration was markedly increased due to a prolongation of the time to peak tension, and in particular, the relaxation phase. 3. The contraction-relaxation cycle of the left atrium showed a marked dependence on the frequency of stimulation. The developed tension and +dT/dtmax showed a progressive increase from 0.5 Hz, reaching peak values at a stimulation rate of 1.5-2.5 Hz, the positive staircase phenomenon. Higher frequencies of stimulation caused a fall in these parameters. Resting tension was unaffected. The time-course of the contraction-relaxation cycle was also frequency-dependent, with both time to peak tension and relaxation time showing a progressive fall from 2.0-3.5 Hz. 4. The addition of CPA (30 microM) caused marked alterations in the frequency-dependence of the contraction-relaxation cycle.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aceto J. F., Condrescu M., Kroupis C., Nelson H., Nelson N., Nicoll D., Philipson K. D., Reeves J. P. Cloning and expression of the bovine cardiac sodium-calcium exchanger. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 1;298(2):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai M., Alpert N. R., MacLennan D. H., Barton P., Periasamy M. Alterations in sarcoplasmic reticulum gene expression in human heart failure. A possible mechanism for alterations in systolic and diastolic properties of the failing myocardium. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):463–469. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuckelmann D. J., Näbauer M., Erdmann E. Intracellular calcium handling in isolated ventricular myocytes from patients with terminal heart failure. Circulation. 1992 Mar;85(3):1046–1055. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.3.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourreau J. P., Abela A. P., Kwan C. Y., Daniel E. E. Acetylcholine Ca2+ stores refilling directly involves a dihydropyridine-sensitive channel in dog trachea. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 1):C497–C505. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.3.C497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Green N. M., Korczak B., MacLennan D. H. Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley N. M., Penefsky Z. J., Litwak R. S. Comparative force-frequency relationships in human and other mammalian ventricular myocardium. Pflugers Arch. 1972;332(4):259–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00588574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain B. K., Levitsky D. O., Fleischer S. Isolation and characterization of canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum with improved Ca2+ transport properties. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6602–6609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesi M., Inesi G. The use of quench reagents for resolution of single transport cycles in sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10370–10377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H. W., Kwan C. Y. Cyclopiazonic acid is a sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-pump inhibitor of rat aortic muscle. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1991 Jan;12(1):53–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeger D. E., Riley R. T. Interaction of cyclopiazonic acid with rat skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Effect on Ca2+ binding and Ca2+ permeability. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 15;38(22):3995–4003. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90679-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwathmey J. K., Copelas L., MacKinnon R., Schoen F. J., Feldman M. D., Grossman W., Morgan J. P. Abnormal intracellular calcium handling in myocardium from patients with end-stage heart failure. Circ Res. 1987 Jul;61(1):70–76. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwathmey J. K., Slawsky M. T., Hajjar R. J., Briggs G. M., Morgan J. P. Role of intracellular calcium handling in force-interval relationships of human ventricular myocardium. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1599–1613. doi: 10.1172/JCI114611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasenfuss G., Mulieri L. A., Leavitt B. J., Allen P. D., Haeberle J. R., Alpert N. R. Alteration of contractile function and excitation-contraction coupling in dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 1992 Jun;70(6):1225–1232. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.6.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W., Noble D. Excitation-contraction coupling and extracellular calcium transients in rabbit atrium: reconstruction of basic cellular mechanisms. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Mar 23;230(1259):163–205. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. R. Rapid preparation of canine cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles by sucrose flotation. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:85–91. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewartowski B., Pytkowski B. Cellular mechanism of the relationship between myocardial force and frequency of contractions. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1987;50(2):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(87)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercadier J. J., Lompré A. M., Duc P., Boheler K. R., Fraysse J. B., Wisnewsky C., Allen P. D., Komajda M., Schwartz K. Altered sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase gene expression in the human ventricle during end-stage heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):305–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI114429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulieri L. A., Hasenfuss G., Leavitt B., Allen P. D., Alpert N. R. Altered myocardial force-frequency relation in human heart failure. Circulation. 1992 May;85(5):1743–1750. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.5.1743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll D. A., Longoni S., Philipson K. D. Molecular cloning and functional expression of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1700476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss H. B., Houser S. R. Sodium-calcium exchange-mediated contractions in feline ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 2):H1161–H1169. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.4.H1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky Z. J., Buckley N. M., Litwak R. S. Effect of temperature and calcium on force-frequency relationships in mammalian ventricular myocardium. Pflugers Arch. 1972;332(4):271–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00588575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter M. Der Einfluss der Natriumionen auf die Beziehung zwischen Frequenz und Kraft der Kontraktion des isolierten Meerschweinchenmyokards. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol Exp Pathol. 1966;254(3):261–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Hambrecht R., Schlierf G., Niebauer J., Hauer K., Neumann J., Hoberg E., Drinkmann A., Bacher F., Grunze M. Regular physical exercise and low-fat diet. Effects on progression of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1992 Jul;86(1):1–11. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler N. W., Jona I., Vegh M., Martonosi A. Cyclopiazonic acid is a specific inhibitor of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17816–17823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler S., Fleischer S. Isolation and characterization of sarcolemmal vesicles from rabbit fast skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:26–36. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Muraki K., Imaizumi Y., Watanabe M. Cyclopiazonic acid, an inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-pump, reduces Ca(2+)-dependent K+ currents in guinea-pig smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):134–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Yue D. T. Intracellular calcium transients underlying the short-term force-interval relationship in ferret ventricular myocardium. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


