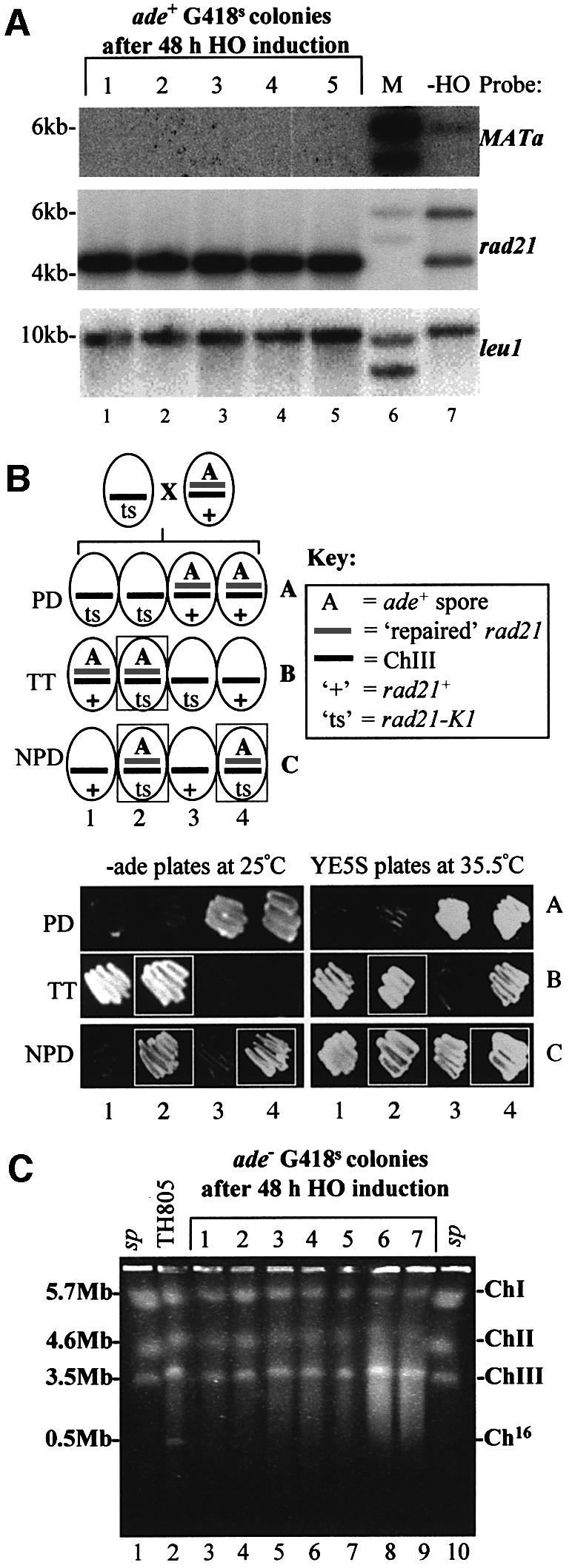
Fig. 3. Analysis of site-specific DSB repair in G418S cells. (A) Southern blot analysis of EcoRI-digested chromosomal DNA from five independent ade+ G418S colonies, obtained after 48 h of HO induction in strain TH844 (lanes 1–5). Chromosomal DNA from TH805 (which lacks pREP81X-HO) was also analysed (lane 7). Southern blot probed with MATa (upper panel), rad21 (middle panel) and leu1 (lower panel). M indicates the DNA size marker (lane 6). (B) A repaired ade+ G418S colony can complement a rad21-K1 mutant. Upper panel: schematic of predicted genotypes from a cross between a ‘ts’ rad21-K1 mutant and an ade+ G418S colony, which contains a repaired rad21 allele on Ch16. The PD (parental ditype), TT (tetra type) and NPD (non-parental ditype) genotypes are shown. Lower panel: examples of dissected PD, TT and NPD tetrads obtained from the above cross with rad21-K1 (TH1017). The ability of the repaired Ch16-rad21 to complement the rad21-K1 mutant was determined by the ability to grow at the restrictive temperature (35.5°C; boxed). Colony coordinates correspond to the predicted genotypes shown above. (C) PFGE analysis of chromosomal DNA from seven individual ade– G418S colonies obtained following DSB induction in a wild-type background (lanes 3–9). Chromosomal DNA from wild-type TH805 (which lacks pREP81X-HO) is shown as a control (lane 2). Schizosaccharomyces pombe commercial markers are shown (lanes 1 and 10).
