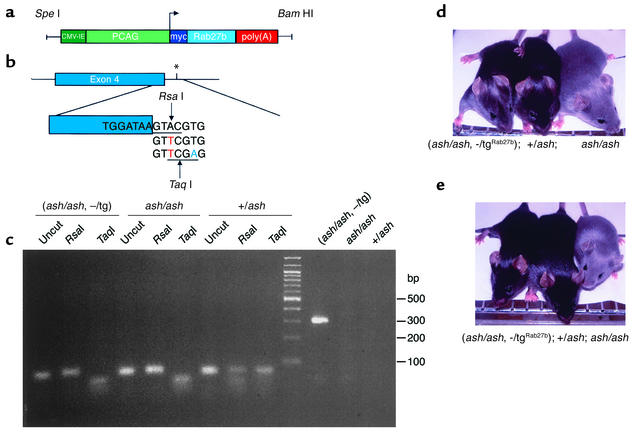
Figure 7.
(a) Organization of the transgenic construct encoding Rab27b under the control of β-actin promoter. The PCAG/mycRab27/β-globin construct contains the CMV enhancer (dark green) and the chicken β-actin promoter sequence (light green) upstream of Rab27a or Rab27b cDNA (light blue), followed by the rabbit β-globin poly(A) sequence (red). (b) Strategy to detect ashen mutation (*). This is an A→T transversion (red) that is present on the third base of the splice donor site downstream of exon 4 (blue). Primers ASH2 (see Methods), introduces a T→A transversion (green). RsaI, which recognizes the sequence GTAC (underlined), cuts the DNA where indicated only in the absence of the ashen mutation. TaqI, which recognizes the sequence TCGA (underlined), cuts the DNA where indicated only if the ashen mutation is present. (c) Mouse genotyping. After PCR amplification the 80 bp product was digested with RsaI and TaqI, which originates one fragment of 50 bp and one fragment of 30 bp. The uncut amplified product is shown as a control. The screening for the presence of the transgene was done as described in Methods, generating a product of 324 bp. The PCR and digestion products were resolved on a 3% agarose gel. The molecular weight of the standards is indicated on the right. (d and e) Photography of representative mice for Rab27b (d) or Rab27a (e) rescue experiment. Littermates resulting from crosses between a homozygous ashen mice with heterozygous transgenic mice were genotyped as above.