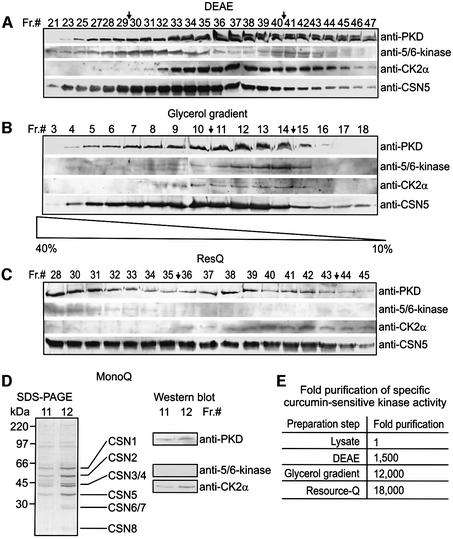
Fig. 1. CK2 and PKD co-purify with the CSN during its preparation from human erythrocytes. (A) Western blots with fractions 21–47 from DEAE column (Seeger et al., 1998). The blots were probed with anti-PKD, anti-5/6-kinase, anti-CK2α and anti-CSN5 antibodies. Fractions 30–40 indicated by arrows were pooled for determination of specific curcumin-sensitive kinase activity [see (E) and Materials and methods] and for further purification. (B) Western blots with fractions 3–18 from a 10 to 40% glycerol gradient using same antibodies as in (A). Fractions 11–14 (arrows) were pooled for further use. (C) Western blots with fractions 28–45 obtained from a RecourceQ column using the same antibodies as in (A). Fractions 36–43 were pooled. (D) SDS–PAGE of 20-µl aliquots of fractions 11 and 12 after MonoQ ion exchange chromatography. Core CSN subunits are indicated. Western blots with the same fractions using anti-PKD, anti-5/6-kinase and anti-CK2α antibodies revealed the presence of CK2α and PKD, but not of 5/6-kinase, in the final CSN preparation. (E) Curcumin-sensitive kinase activity co-purifies with the CSN. Fixing the kinase activity in the lysate to 1, a 18 000-fold co-purification of CSN-associated kinase activity was achieved by the final preparation steps.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.