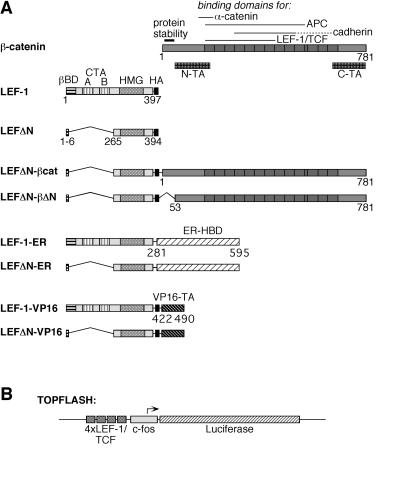
Figure 1.
Structure of LEF-1 fusion proteins. (A) Schematic representation of β-catenin, LEF-1, and LEF-1-fusions. On the β-catenin molecule, several specific domains are marked: an amino-terminal region responsible for the instability of the protein and two transactivating domains, N-TA and C-TA. The armadillo repeats are represented as dark boxes. On the LEF-1 molecule, the β-catenin-binding domain (βBD), two context-dependent transactivation domains (CTA-A and CTA-B), and the HMG-box mediating DNA binding are marked. The HA-epitope tag on all constructs is represented by a black box. The hormone-binding domain (HBD) of the human ER and the carboxyl-terminal transactivation (TA) domain of the herpes simplex virus VP16 protein are shown as hatched boxes. Amino acid positions of the termini of the various protein domains are given. (B) Schematic representation of the Topflash reporter construct. Expression of the luciferase gene (hatched bar) in this plasmid is driven by the c-fos minimal promoter (gray box) and four copies of a LEF-1/TCF consensus binding motif (dark gray boxes).