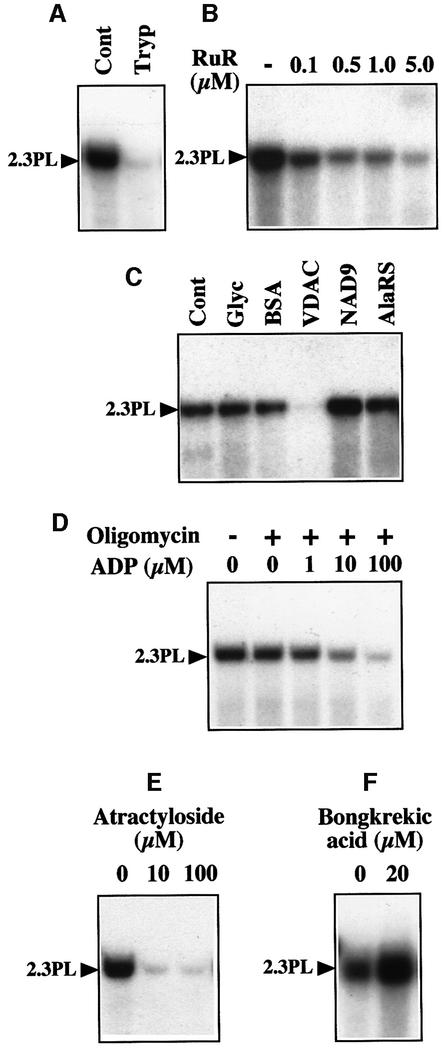
Fig. 5. Mitochondrial uptake of DNA is likely to involve VDAC/ANT complexes. (A) DNA uptake requires surface-accessible protein(s). The labeled maize 2.3 kb plasmid was incubated in the presence of mock-pretreated (Cont) or trypsin-pretreated (Tryp) potato mitochondria. (B) DNA uptake is inhibited by Ruthenium Red. Mitochondrial incorporation of labeled maize 2.3 kb plasmid was tested in the presence of increasing concentrations of Ruthenium Red (RuR). (C) DNA uptake is inhibited by antibodies against the VDAC. Incorporation of labeled maize 2.3 kb plasmid was tested in the presence of mock-treated mitochondria (Cont), mitochondria pretreated with BSA, or mitochondria pretreated with a polyclonal antiserum against the VDAC, NAD9 or alanyl-tRNA synthetase (AlaRS). As the antisera used contained 50% (v/v) glycerol, a control assay was also run in the presence of the relevant amount of glycerol (Glyc). (D) DNA uptake is inhibited by ADP. Mitochondrial incorporation of labeled maize 2.3 kb plasmid was tested in the presence of increasing concentrations of ADP and a constant concentration (10 µg/ml) of oligomycin (+). (E and F) DNA uptake is inhibited by atractyloside, but enhanced by bongkrekic acid. Mitochondrial incorporation of labeled maize 2.3 kb plasmid was tested in the presence of atractyloside (E) or bongkrekic acid (F). Migration of the incorporated plasmid (2.3PL) is indicated.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.