Figure 1.
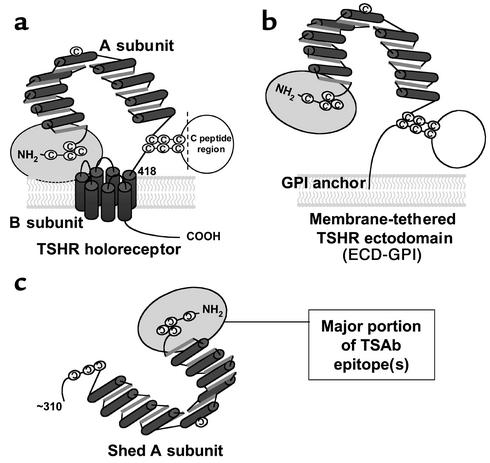
Schematic representation of different forms of the TSHR. (a) TSH holoreceptor. Intramolecular cleavage of the single polypeptide chain is followed by removal of the C peptide region, with the A subunit remaining tethered to the membrane-spanning B subunit by disulfide bonds. The cylinders depict the α helices in the nine leucine-rich repeats in the A subunit, as well as the seven transmembrane segments of the B subunit. The ectodomain comprises the entire A subunit and the extracellular region of the B subunit. The ectodomain enters the plasma membrane at approximately amino acid residue 418. A critical domain in the TSAb epitope(s) involves the cysteine-rich area at the extreme N terminus of the TSHR and is shown by the gray oval. (b) TSHR ectodomain tethered to the plasma membrane by a GPI anchor (ECD-GPI). This construct involved the attachment after TSHR codon 412 of a 39–amino acid sequence containing a signal for GPI attachment (31). The putative GPI attachment site of the anchor is at codon 425. Because of the additional length of the ectodomain prior to insertion into the membrane, and because the GPI anchor only traverses the outer leaf of the plasma membrane, the TSHR ectodomain is shown in a more “open” orientation relative to the wild-type TSHR. (c) Shed A subunit. The exact site of cleavage has not been established, but is approximately at amino acid residue 310. The purified TSHR-289 preparation used in this study is truncated at TSHR amino acid residue 289 and therefore comprises nearly the entire A subunit.