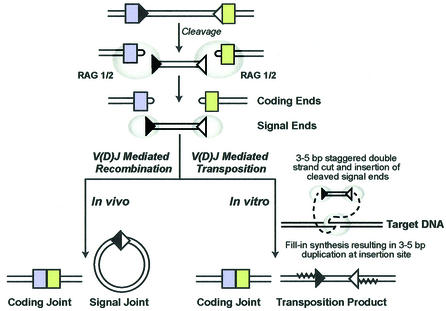
Fig. 1. V(D)J recombinase-mediated rearrangements. The steps involved in V(D)J recombination include site-specific recognition and cleavage at 12 bp RSS (black triangles) and 23 bp RSS (white triangles) sites by RAG1/2 (gray ovals), generating the hairpin coding ends (colored boxes) and the signal ends. Non-homologous end joining proteins process the coding ends. The result is a ligated coding joint that forms the functional gene product and a circularized signal joint. RAG1/2 are also capable of mediating transposition in vitro by strand transfer of the signal ends into a non-RSS target site. Transposition involves a staggered double-strand cut by RAG1/2, insertion of the signal ends, and fill-in synthesis resulting in a 3–5 bp target site duplication. This figure is adapted from Lewis and Wu (2000).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.