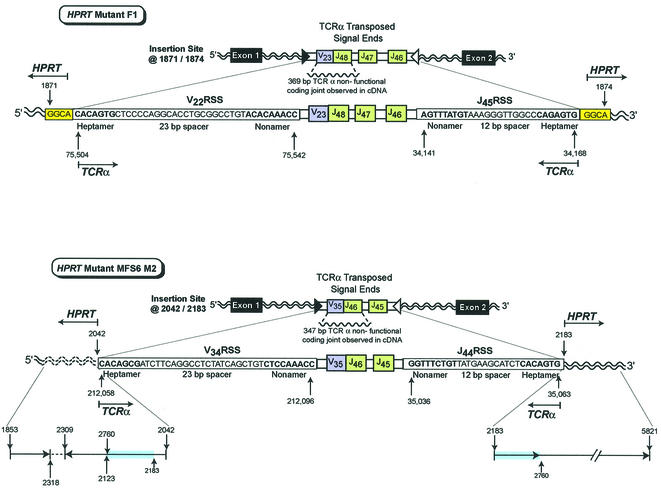
Fig. 2. In vivo transposition of TCRα V-J signal ends from chromosome 14 into the HPRT gene on the X chromosome. HPRT mutant F1 contains transposed TCRα signal ends containing ∼16.8 kbp of intervening sequence that includes the V22 RSS (heptamer–23 bp spacer–nonamer), a V23 joined to J48 non-functional coding joint, J47, J46, and the J45 RSS (nonamer–12 bp spacer–heptamer) inserted into HPRT at bases 1871/1874. The insertion site is located in intron 1 of the HPRT gene. A 4 bp target site duplication, GGCA (1871–1874), is shown at both sides of the insertion. HPRT mutant MFS6 M2 contains transposed TCRα signal ends containing ∼16.1 kbp of intervening sequence that includes the V34 RSS (heptamer–23 bp spacer–nonamer), a V35 joined to J46 non-functional coding joint, J45, and the J44 RSS (nonamer–12 bp spacer–heptamer) inserted into HPRT at 2042/2183. The insertion site is located in intron 1 of the HPRT gene. Reading 5′ to 3′, the 5′ insertion site includes bases 1853–2318 followed by the inverted sequence 2309–2123 and 2760–2042. There is normal sequence at the 3′ HPRT insertion site from 2183 to 5821 that includes the same duplication of bases from 2183 to 2760 observed at the 5′ insertion site. HPRT bases that are duplicated are highlighted in blue. The inverted segment is shown by an arrow in the 3′ to 5′ direction.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.