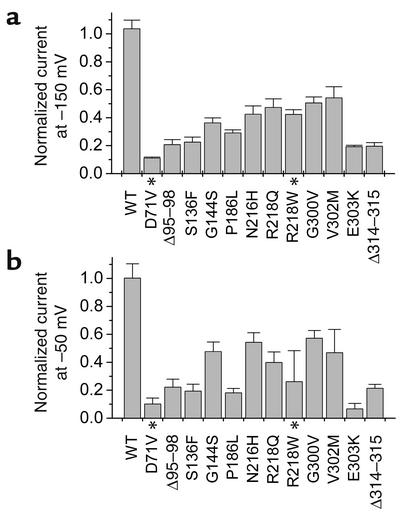
Figure 2.
AS-associated mutations in KCNJ2 cause dominant-negative suppression of Kir2.1 channel function. (a) Peak current induced by coexpression of mutant and WT KCNJ2 (0.8 ng/oocyte for each) at –150 mV was normalized to currents induced by expression of WT KCNJ2 (0.8 ng/oocyte). Current magnitude is reported at –150 mV because this gives a measure of conductance in the absence of rectification. KCNJ2 mutations caused variable degrees of dominant-negative suppression of channel function. Note that a haploinsufficiency effect would result in current magnitude equal to that of the WT group. (b) Normalized current at –50 mV. KCNJ2 mutations also reduce magnitude of outward current in a dominant-negative manner. *D71V and R218W data were obtained from ref. 6.