Abstract
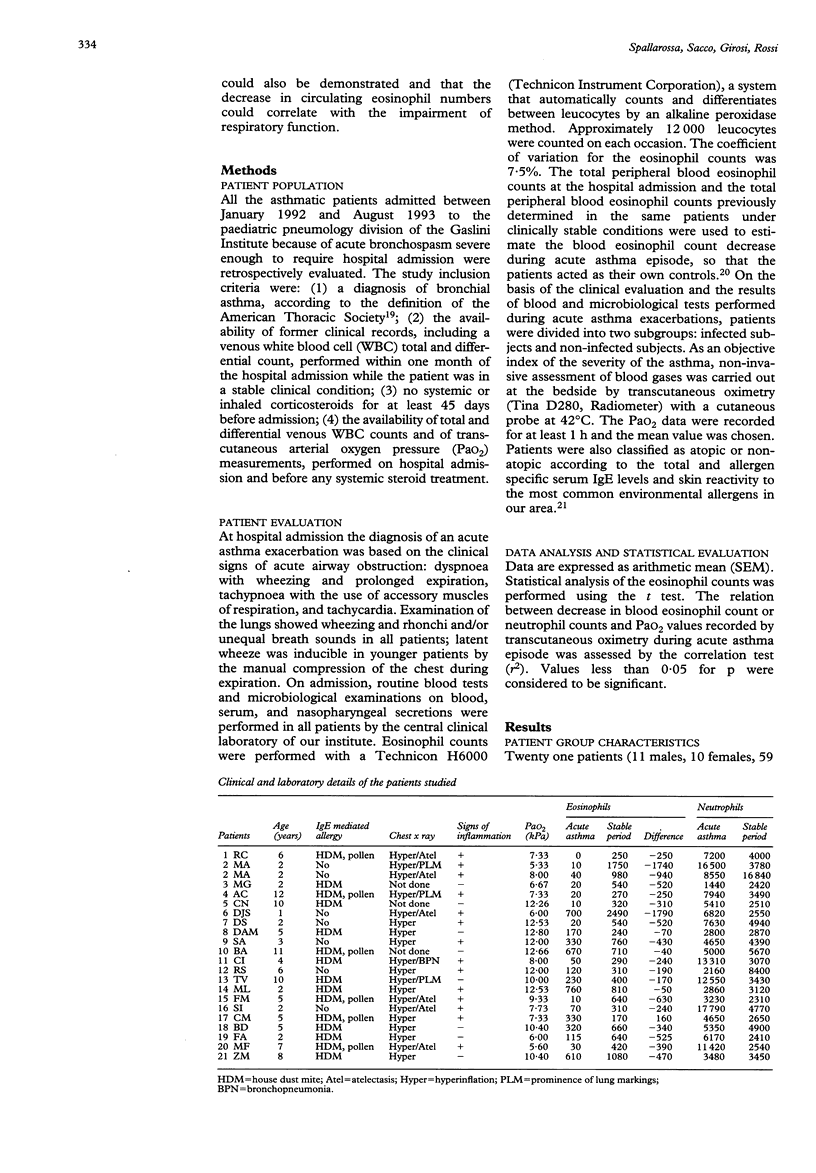
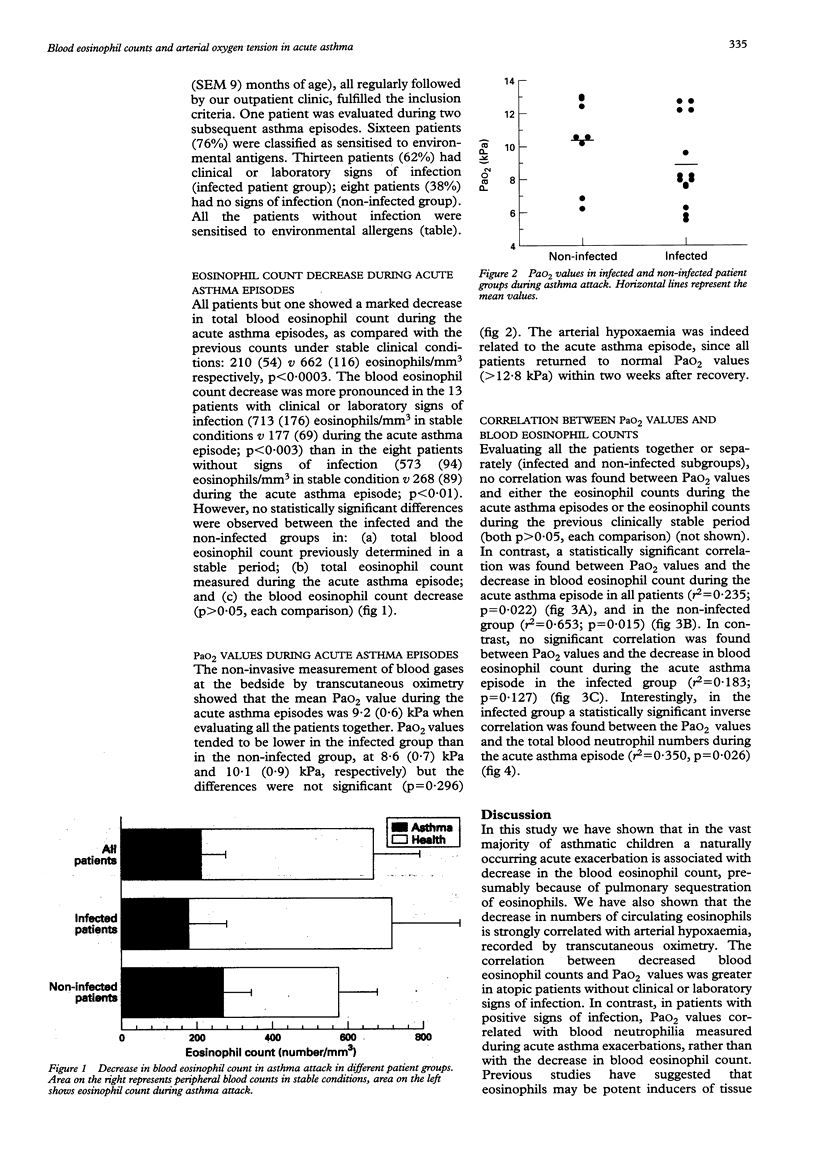
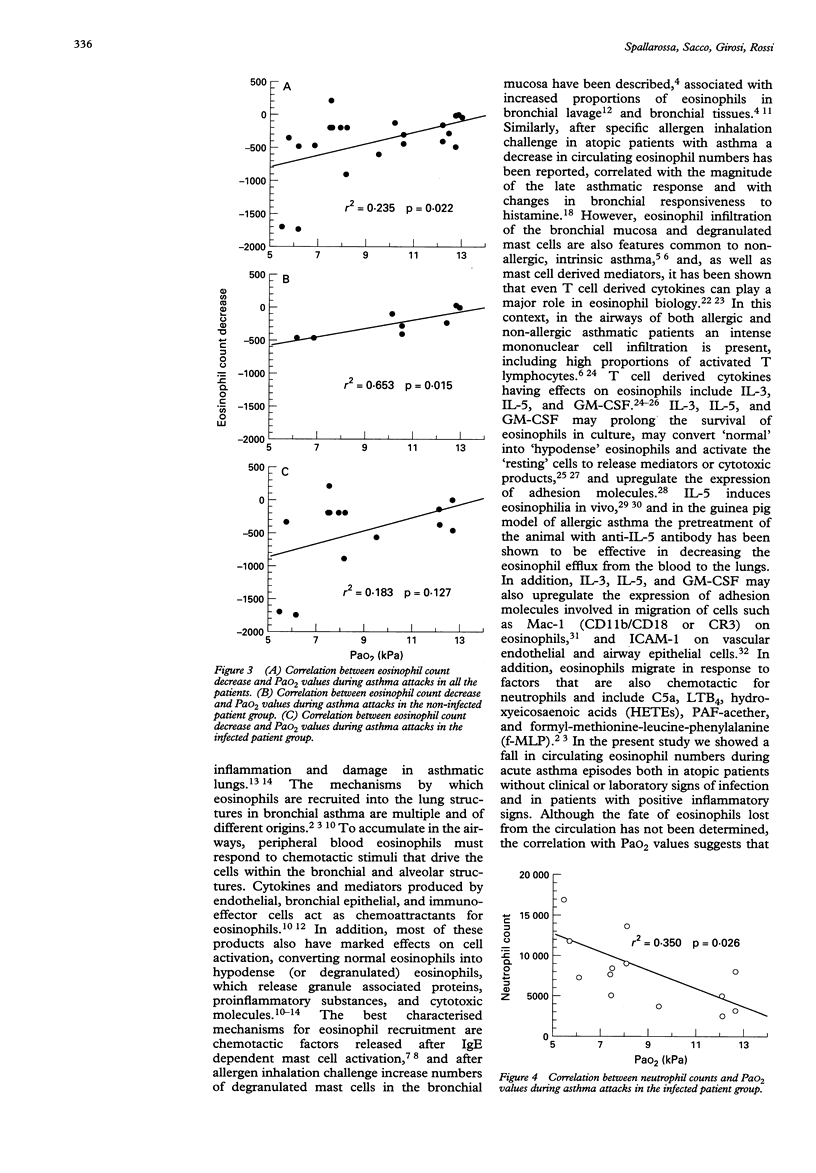
OBJECTIVE--To investigate whether during acute asthma episodes a decrease in blood eosinophil count could correlate with the severity of the disease. DESIGN--Prospective study on paediatric asthmatic patients admitted for acute asthma exacerbation between January 1992 and August 1993. All patients were regularly followed up in an outpatient clinic and had had a complete clinical evaluation < 1 month before admission. SETTING--Pulmonary division of the G Gaslini paediatric research institute, Genoa, Italy. SUBJECTS--21 asthmatic patients, 59 (SEM 9) months of age, admitted for acute asthma exacerbation. On the basis of clinical evaluation and the results of blood and microbiological tests performed during acute asthma exacerbations, patients were divided into two subgroups: infected (n = 13) and non-infected (n = 8). RESULTS--All but one of the patients showed a marked decrease in blood eosinophil count during the acute asthma episode, in comparison with recent count (< 1 month before admission) obtained in clinically stable conditions: 662 (116) v 210 (54) eosinophils/mm3, p < 0.0003. The decrease in the eosinophil count was more pronounced in the infected patients than in the non-infected patients, but the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). Similarly, transcutaneous arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2) values measured during acute asthma exacerbations tended to be lower in infected patients, without, however, reaching statistical significance: 8.6 (0.7) v 10.1 (0.9) kPa, p > 0.05). The correlation between the decrease in blood eosinophil count and PaO2 during the acute asthma exacerbations was significant in all the patients (r2 = 0.235, p = 0.022) and in the non-infected patients (r2 = 0.653, p = 0.015), but not in infected patients. In this latter subgroup, a significant negative correlation was found between blood neutrophil counts during acute asthma exacerbations and PaO2 (r2 = 349, p = 0.026). CONCLUSIONS--During acute asthma exacerbations in atopic patients without clinical evidence of infection, the decrease in blood eosinophil count correlates significantly with the decrease in PaO2, further supporting the role of eosinophils in allergic asthma.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. J., Corrette S. E., Rosenberg H. F., Bennett J. C., Mastrianni D. M., Nicholson-Weller A., Weller P. F., Chin D. T., Tenen D. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase). Similarities to IgE binding proteins and the S-type animal lectin superfamily. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):456–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. M., Meng Q., Robinson D. S., Hamid Q., Kay A. B., Durham S. R. Increases in activated T lymphocytes, eosinophils, and cytokine mRNA expression for interleukin-5 and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in bronchial biopsies after allergen inhalation challenge in atopic asthmatics. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;8(1):35–42. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. M., Menz G., Storz C., Robinson D. S., Bradley B., Jeffery P. K., Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Identification of T lymphocytes, macrophages, and activated eosinophils in the bronchial mucosa in intrinsic asthma. Relationship to symptoms and bronchial responsiveness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Aug;146(2):500–506. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.2.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. S., Weller P. F. Airway eosinophils and lymphocytes in asthma. Birds of a feather? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jun;145(6):1246–1248. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.6.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusasco V., Crimi E., Gianiorio P., Lantero S., Rossi G. A. Allergen-induced increase in airway responsiveness and inflammation in mild asthma. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Dec;69(6):2209–2214. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.69.6.2209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck E. J., Hirst E. M., Sanderson C. J. Human interleukin-5 (IL-5) regulates the production of eosinophils in human bone marrow cultures: comparison and interaction with IL-1, IL-3, IL-6, and GMCSF. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1504–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson W. O., Craddock C. F., Benson M. K., Durham S. R. Falls in peripheral eosinophil counts parallel the late asthmatic response. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):458–462. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan C. J., Kay A. B. T cells and eosinophils in the pathogenesis of asthma. Immunol Today. 1992 Dec;13(12):501–507. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crimi E., Balbo A., Milanese M., Miadonna A., Rossi G. A., Brusasco V. Airway inflammation and occurrence of delayed bronchoconstriction in exercise-induced asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Aug;146(2):507–512. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.2.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crimi E., Chiaramondia M., Milanese M., Rossi G. A., Brusasco V. Increased numbers of mast cells in bronchial mucosa after the late-phase asthmatic response to allergen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Dec;144(6):1282–1286. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.6.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Monchy J. G., Kauffman H. F., Venge P., Koëter G. H., Jansen H. M., Sluiter H. J., De Vries K. Bronchoalveolar eosinophilia during allergen-induced late asthmatic reactions. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):373–376. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G., Maggi E., Parronchi P., Chrétien I., Tiri A., Macchia D., Ricci M., Banchereau J., De Vries J., Romagnani S. IL-4 is an essential factor for the IgE synthesis induced in vitro by human T cell clones and their supernatants. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4193–4198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent L. A., Strath M., Mellor A. L., Sanderson C. J. Eosinophilia in transgenic mice expressing interleukin 5. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1425–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J. The eosinophil and bronchial asthma: current understanding. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Feb;85(2):422–436. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90151-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Burd P. R., Galli S. J. Mast cells as a source of multifunctional cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90176-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundel R. H., Letts L. G., Gleich G. J. Human eosinophil major basic protein induces airway constriction and airway hyperresponsiveness in primates. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1470–1473. doi: 10.1172/JCI115155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B. Eosinophils as effector cells in immunity and hypersensitivity disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Oct;62(1):1–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas A. M., Marcotte G. V., Schleimer R. P. Human endothelial cells prolong eosinophil survival. Regulation by cytokines and glucocorticoids. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3978–3984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Sanderson C. J., Gamble J. R., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is a selective activator of human eosinophil function. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):219–224. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luksza A. R., Jones D. K. Comparison of whole-blood eosinophil counts in extrinsic asthmatics with acute and chronic asthma. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 30;285(6350):1229–1231. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6350.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren J. D., Davey R. T., Jr, Lundgren B., Mullol J., Marom Z., Logun C., Baraniuk J., Kaliner M. A., Shelhamer J. H. Eosinophil cationic protein stimulates and major basic protein inhibits airway mucus secretion. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Mar;87(3):689–698. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90390-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi Y., Motojima S., Fukuda T., Makino S. Airway hyperresponsiveness, increased intracellular spaces of bronchial epithelium, and increased infiltration of eosinophils and lymphocytes in bronchial mucosa in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jun;145(6):1469–1476. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.6.1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. S., Hamid Q., Ying S., Tsicopoulos A., Barkans J., Bentley A. M., Corrigan C., Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Predominant TH2-like bronchoalveolar T-lymphocyte population in atopic asthma. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 30;326(5):298–304. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201303260504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrbach M. S., Wheatley C. L., Slifman N. R., Gleich G. J. Activation of platelets by eosinophil granule proteins. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1271–1274. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G. A., Crimi E., Lantero S., Gianiorio P., Oddera S., Crimi P., Brusasco V. Late-phase asthmatic reaction to inhaled allergen is associated with early recruitment of eosinophils in the airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Aug;144(2):379–383. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spry C. J., Kay A. B., Gleich G. J. Eosinophils 1992. Immunol Today. 1992 Oct;13(10):384–387. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90085-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Bode E., Boer L., Hansel T. T., Blaser K., Virchow J. C., Jr Allergic and nonallergic asthmatics have distinct patterns of T-cell activation and cytokine production in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):109–115. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren D. J., Moore M. A. Synergism among interleukin 1, interleukin 3, and interleukin 5 in the production of eosinophils from primitive hemopoietic stem cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):94–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


