Abstract
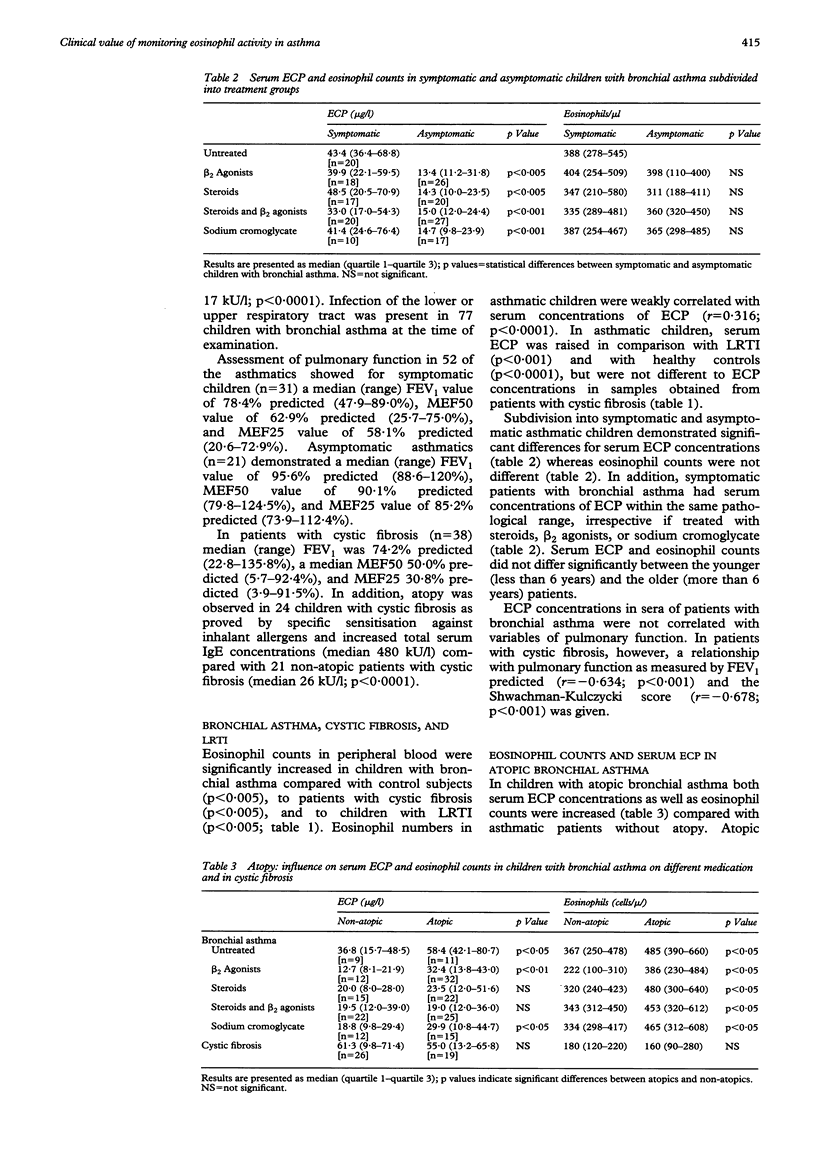
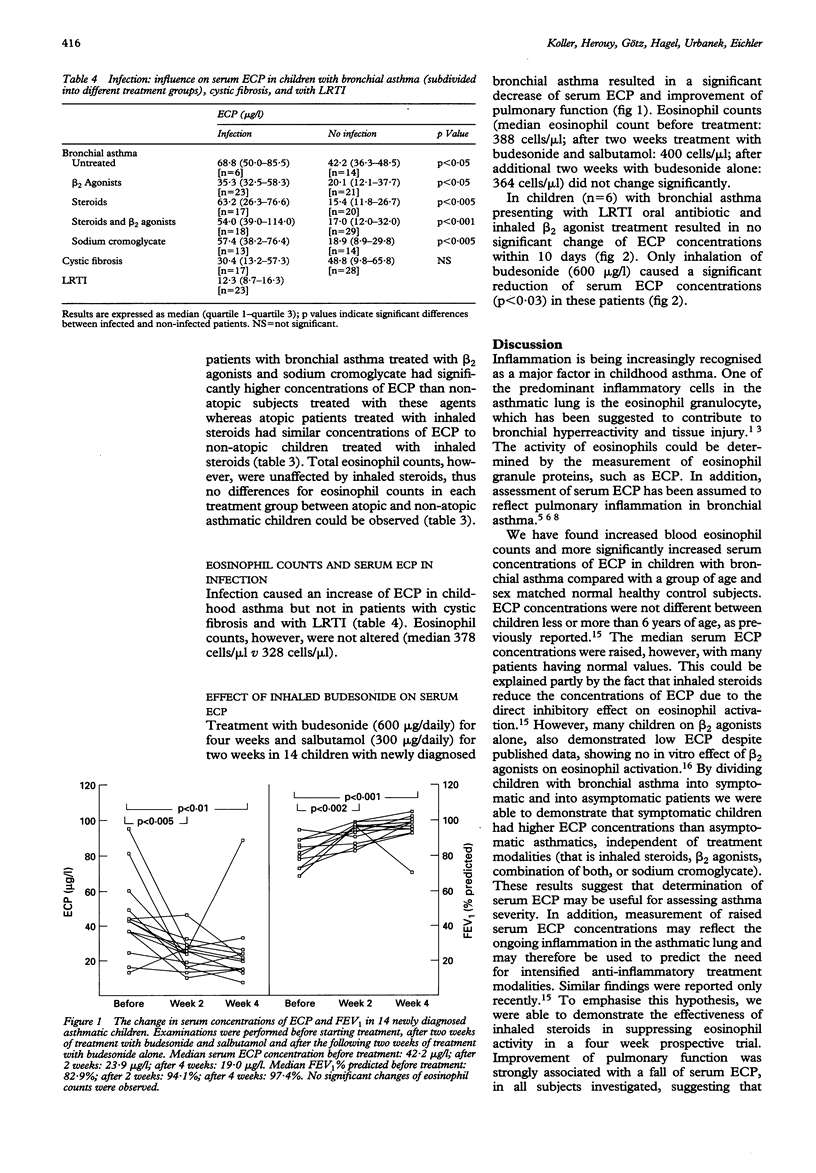
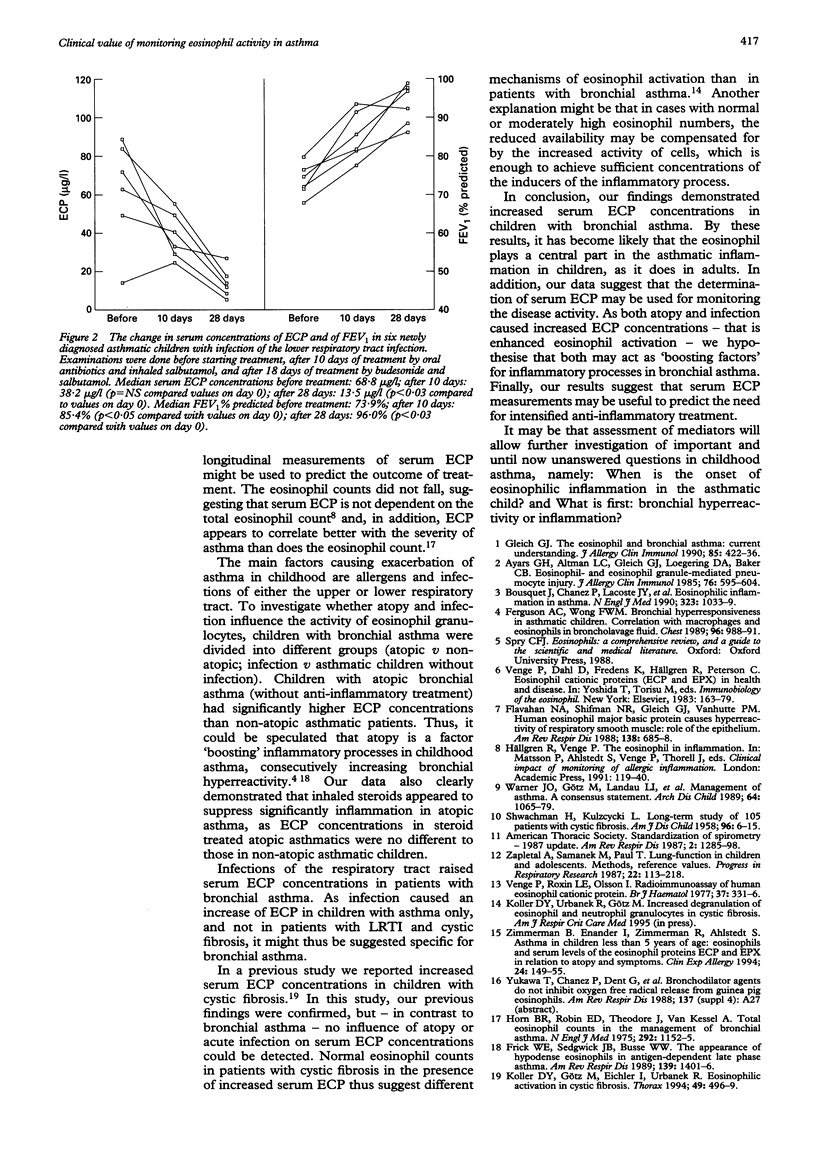
To evaluate the use of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) in monitoring disease activity in childhood asthma, serum ECP in 175 asthmatic children was assessed. Forty five patients with cystic fibrosis, 23 with lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI), and 87 healthy children were used as controls. Serum ECP concentrations (34.3 micrograms/l v 9.8 micrograms/l) were significantly higher in children with bronchial asthma than in healthy control subjects. In symptomatic patients with asthma serum ECP concentrations were increased compared with those from asymptomatic patients (40.2 micrograms/l v 14.4 micrograms/l), irrespective of treatment modalities (that is steroids, beta 2 agonists, or sodium cromoglycate). Moreover, atopy and infection appeared to be factors enhancing eosinophil activity in bronchial asthma as measured by serum ECP (58.4 micrograms/l v 36.8 micrograms/l and 68.8 micrograms/l v 42.2 micrograms/l, respectively). In a longitudinal trial, antiasthmatic treatment modalities (that is steroids) reduced serum ECP within four weeks (42.2 micrograms/l v 19.0 micrograms/l). In conclusion, the data indicate that (1) eosinophils also play a central part in childhood asthma; (2) serum concentrations of ECP in children with bronchial asthma are related to the disease severity and may thus be used for monitoring inflammation in childhood asthma; (3) eosinophil activity appears to be enhanced by atopy and infection; and (4) longitudinal measurements of serum ECP concentrations may be useful for optimising anti-inflammatory treatment in children with bronchial asthma.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayars G. H., Altman L. C., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Baker C. B. Eosinophil- and eosinophil granule-mediated pneumocyte injury. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 Oct;76(4):595–604. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90781-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet J., Chanez P., Lacoste J. Y., Barnéon G., Ghavanian N., Enander I., Venge P., Ahlstedt S., Simony-Lafontaine J., Godard P. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 11;323(15):1033–1039. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010113231505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. C., Wong F. W. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic children. Correlation with macrophages and eosinophils in broncholavage fluid. Chest. 1989 Nov;96(5):988–991. doi: 10.1378/chest.96.5.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A., Slifman N. R., Gleich G. J., Vanhoutte P. M. Human eosinophil major basic protein causes hyperreactivity of respiratory smooth muscle. Role of the epithelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Sep;138(3):685–688. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick W. E., Sedgwick J. B., Busse W. W. The appearance of hypodense eosinophils in antigen-dependent late phase asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jun;139(6):1401–1406. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.6.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J. The eosinophil and bronchial asthma: current understanding. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Feb;85(2):422–436. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90151-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn B. R., Robin E. D., Theodore J., Van Kessel A. Total eosinophil counts in the management of bronchial asthma. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 29;292(22):1152–1155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505292922204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller D. Y., Götz M., Eichler I., Urbanek R. Eosinophilic activation in cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 1994 May;49(5):496–499. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.5.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHWACHMAN H., KULCZYCKI L. L. Long-term study of one hundred five patients with cystic fibrosis; studies made over a five- to fourteen-year period. AMA J Dis Child. 1958 Jul;96(1):6–15. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1958.02060060008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venge P., Roxin L. E., Olsson I. Radioimmunoassay of human eosinophil cationic protein. Br J Haematol. 1977 Nov;37(3):331–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb01003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. O., Götz M., Landau L. I., Levison H., Milner A. D., Pedersen S., Silverman M. Management of asthma: a consensus statement. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Jul;64(7):1065–1079. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.7.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman B., Enander I., Zimmerman R., Ahlstedt S. Asthma in children less than 5 years of age: eosinophils and serum levels of the eosinophil proteins ECP and EPX in relation to atopy and symptoms. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994 Feb;24(2):149–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1994.tb00212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


