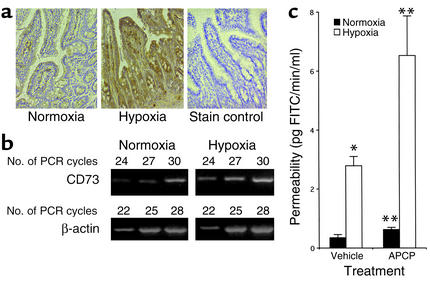
Figure 6.
Role of hypoxia-induced CD73 in vivo. BL/6/129 mice were gavaged with vehicle (PBS) or APCP (2 mg/100 g body weight, based on previous work in rats [ref. 27]) in combination with permeability tracer (60 mg/100 g body weight of FITC-labeled dextran, mol wt 4,000 daltons, as indicated) and exposed to ambient hypoxia (8% O2, 92% N2) or ambient room air for 4 hours. (a) Small-intestine hypoxia was monitored by localization of EF5 relative to the normoxia control. Also shown is a stain control (primary antibody omitted). (b) Total RNA was isolated from mucosal scrapings (enriched with epithelial cells), and CD73 mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR using semiquantitative analysis (increasing cycle numbers, as indicated). As shown, β-actin transcript was determined in parallel and used as an internal standard. (c) Serum analysis of FITC concentration was performed as an indicator of intestinal permeability. Data are mean permeability ± SEM pooled from four to six animals per condition. *P < 0.025 compared with normoxia in vehicle controls; **P < 0.05 for APCP treatment compared with animals exposed to vehicle only.