Figure 3.
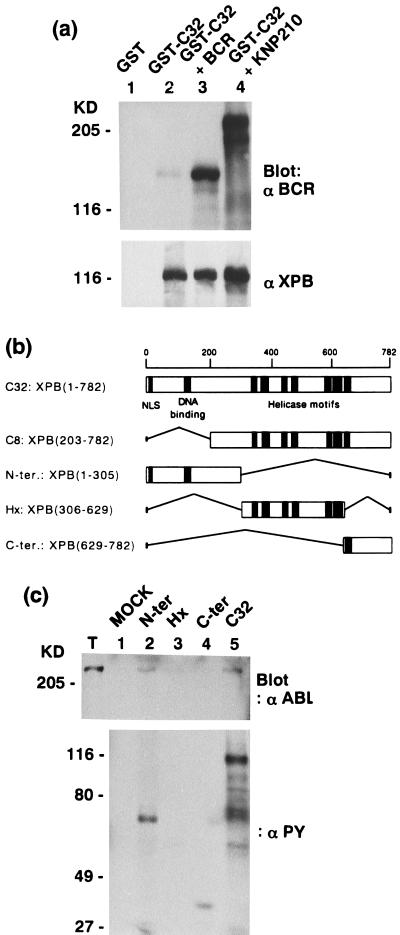
(a) Tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for the XPB/P210 BCR-ABL interaction. Glutathione Sepharose-bound preparations from 27–1 cells overexpressing GST (lane 1), GST-C32 (lane 2), GST-C32 with BCR (lane 3), and GST-C32 with a kinase negative mutant of P210 BCR-ABL (KN P210) (lane 4) were subjected to anti-BCR (Upper) and anti-XPB (Lower) Western blotting. (b) Schematic representation of the isolated XPB clones (C8 and C32) and three XPB fragments (N-ter, Hx, and C-ter) constructed from C32. The putative nuclear localization signal (NLS), the potential DNA-binding domain, and conserved helicase motifs are indicated. The amino acid numbers are shown on the top. (c) XPB N-ter and C-ter fragments were tyrosine-phosphorylated by P210 BCR-ABL. E. coli-expressed and glutathione Sepharose-bound GST (lane 1, MOCK), GST-N-ter (lane 2), GST-Hx (lane 3), GST-C-ter (lane 4) as shown in b, and GST-C32 (lane 5) were incubated with total cell lysates from Sf9 cells infected with P210 BCR-ABL baculovirus (T) to allow binding. After washing, each sample was subjected to an in vitro kinase assay followed by anti-ABL (Upper) and anti-PY (Lower) Western blotting.