Figure 6.
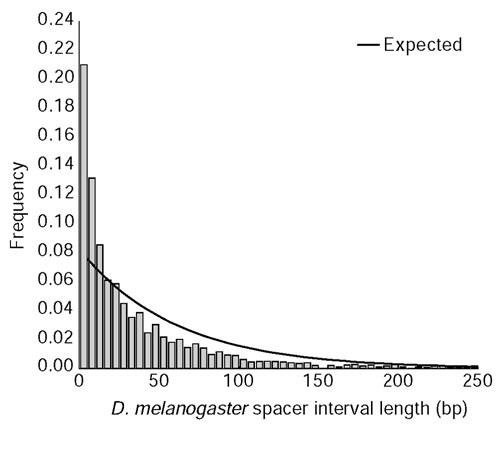
Frequency distribution of spacer interval lengths separating CNCSs between D. melanogaster and D. pseudoobscura. Plotted is a histogram of the length in D. melanogaster of 'nonconserved' spacer interval sequences between CNCSs identified using VISTA (10-bp window, 90% identity). Spacer intervals separating a CNCS and a conserved coding segment, or between two conserved coding segments were omitted from this analysis. Note that only spacer interval lengths less than 250 bp are displayed for clarity. Solid lines represent the expectation under an exponential distribution using an estimate of the rate parameter λ based on the inverse of the mean spacer interval length to be 0.0165. The null hypothesis that spacer interval lengths are exponentially distributed can be rejected (χ2 = 2,040.1, df = 30, p < 10-6), indicating that Drosophila CNCSs are non-randomly spaced.
