Figure 4.
Visualization of Cellulose Microfibrils in the Innermost Layer of Fiber Cell Walls.
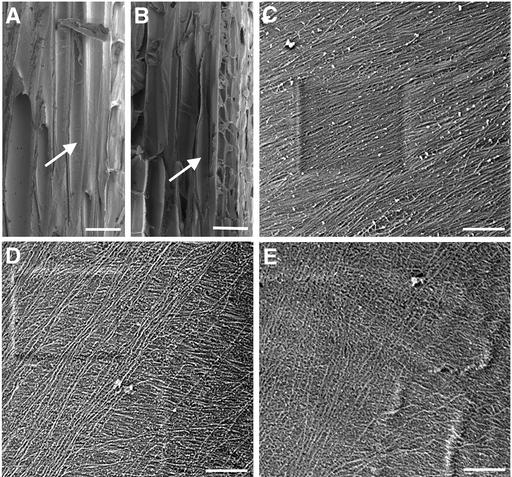
Mature stems were sectioned longitudinally through interfascicular fiber cells, and the innermost layer of microfibrils in fiber cell walls was visualized using a field emission scanning electron microscope. The vertical direction of the cellulose microfibril images corresponds to the long axis of the fiber cells. The square marks in (C) and (D) are the result of beam focusing.
(A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of interfascicular regions of stems of the wild type (A) and fra1 (B) showing representative fiber cells (arrows) that were used for cellulose microfibril visualization.
(C) Cellulose microfibrils in the middle part of a wild-type fiber cell showing their parallel alignment in a small angle relative to the transverse orientation.
(D) and (E) Cellulose microfibrils in the middle parts of fra1 fiber cells showing their aberrantly oriented pattern with various directions.
Bars = 25 μm in (A) and (B) and 0.5 μm in (C) to (E).