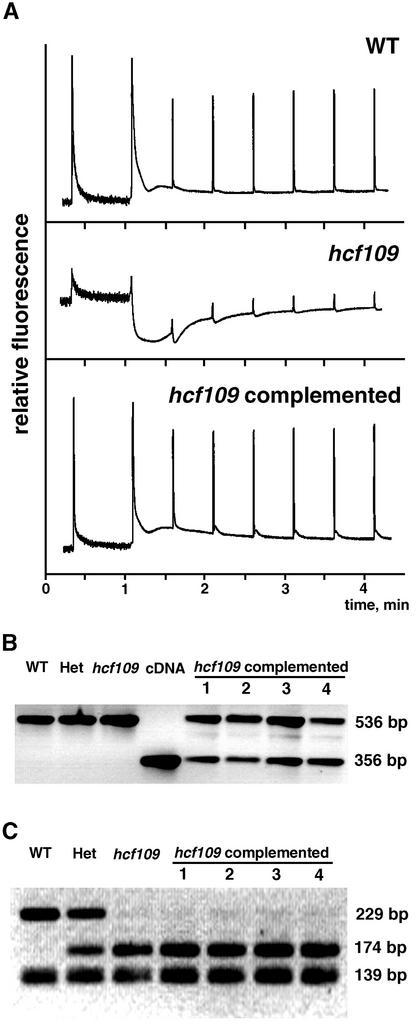
Figure 3.
Complementation of hcf109 with the atprfB cDNA.
(A) Chlorophyll fluorescence induction of wild-type (WT) and mutant plants and complemented lines. Fluorescence characteristics of complemented mutant lines were identical to those of the wild type.
(B) Amplification of genomic DNA (using primers ex1-f and ex3-r [see Methods]) for wild-type plants, heterozygous plants (Het), mutant plants (hcf109), sulfadiazine-resistant transformants 1 to 4, and the corresponding cDNA region of atprfB. Transformant lines 1 to 4 show the presence of the cDNA in the genome.
(C) Tru9I-digested PCR products (with primers in2-f and ex4-r [see Methods]) of atprfB from pooled DNA in wild-type, heterozygous, and mutant plants and individually selected transformant plants 1 to 4. Viable lines 1 to 4 were homozygous for the hcf109 mutation. Several restriction products of <50 bp are not shown.