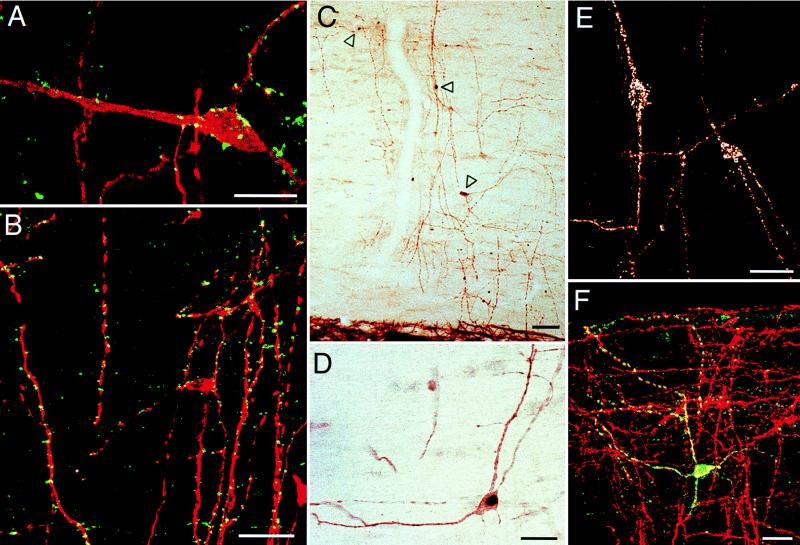
Figure 3.
Sagittal sections of the rat lumbar spinal cord provide information on the functional nature of the neurons of the DC white matter. (A) Labeling for synaptophysin (green) reveals a dense somatic and dendritic synaptic input to the DC neurons (stained for NK-1 receptor; red). (B) A large proportion of the synaptic input to the neurons (stained for MAP-2; red) are GABAergic as they express the GABA vesicle transporter (green). (C and D) Direct CSF injection of the GABAA receptor antagonist, bicuculline, induces Fos expression (black nucleus; arrowheads in C) in approximately 50% of the DC neurons (identified by the brown MAP-2 immunoreaction product). (E) Direct CSF injection of SP induces internalization of the NK-1 receptor in approximately one-third of the DC neurons. The receptor is concentrated in cytoplasmic endosomes. (F) Approximately 20% of the neurons (stained for MAP-2; red) express neuronal nitric oxide synthase (green). In A, B, and F, superimposition of the confocal images produces a yellow image where the immunostaining of two antigens overlaps. (Bars: 25 μm, A; and 50 μm, B–F.)