Figure 3.
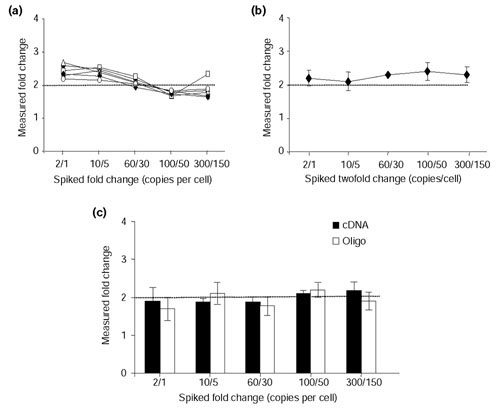
Assessment of sensitivity and reproducibility within and between slides, using the Arabidopsis controls. In vitro transcribed cRNA from a set of five Arabidopsis gene constructs (Ra, Cab, rbcL, Ltp4 and Ltp6) was spiked at varying levels into rat heart and brain RNA (that is, 2/1 represents two copies per cell and one copy per cell of Ra cRNA spiked into heart and brain RNA, respectively). Cy3- and Cy5-labeled targets were hybridized to rat arrays containing Arabidopsis 70-mer and PCR amplicon probes. (a) Intra-slide measurements. Arabidopsis cRNAs were added into the labeling reactions to assess the ability of oligonucleotide probes to discriminate twofold changes. The measured fold-change values are shown for each Arabidopsis target hybridizing to its complementary probe printed across six different sectors of an array. Values derived from a particular sector are represented by an open triangle, open square, open circle, closed circle, closed diamond or closed square. Ra, Cab, rbcL, Ltp4 and Ltp6 cRNAs were differentially spiked at 2/1, 10/5, 60/30, 100/50 and 300/150 copies per cell, respectively. Results are representative of four independent hybridizations. (b) Inter-slide measurements. Arabidopsis cRNAs were spiked into the labeling reactions to evaluate slide-to-slide reproducibility of oligonucleotide probes to discriminate twofold differences. The averaged result from four independent experiments is shown. (c) Comparison of Arabidopsis oligonucleotide and PCR amplicon probes printed on the same array to discriminate twofold changes. Data shown are the mean ± SD of five independent experiments.
