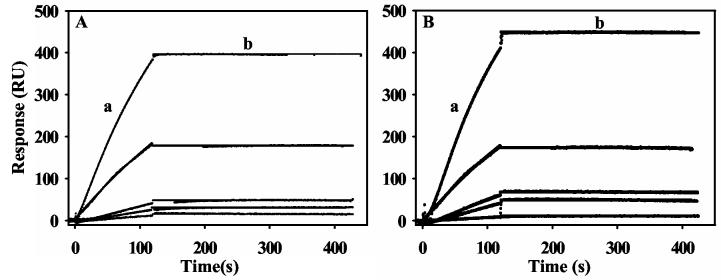
Figure 2.
SPR sensorgrams of the association and dissociation kinetics of proline and sodium dithionite reduced PutA-lipid binding. Panel A: From bottom to top, increasing concentrations of PutA (2.5, 5, 10, 20, and 40 nM) in the presence of 5 mM proline (HEPES-N buffer, pH 7.4) were injected onto a L1 chip coated with E. coli polar lipid vesicles. Panel B: From bottom to top, increasing concentrations of PutA (2.5, 5, 10, 20, and 40 nM) in the presence of 10 mM sodium dithionite (HEPES-N buffer, pH 7.4) were injected onto a L1 chip coated with E. coli polar lipid vesicles. Association phase (a) corresponds to the injection of PutA at 60 μl/min for 120 s and the dissociation phase (b) corresponds to the flow of HEPES-N buffer at 60 μl/min for 300 s. The data were fit by global analysis to a 1:1 Langmuir binding isotherm. Signals from the control surface have been subtracted.