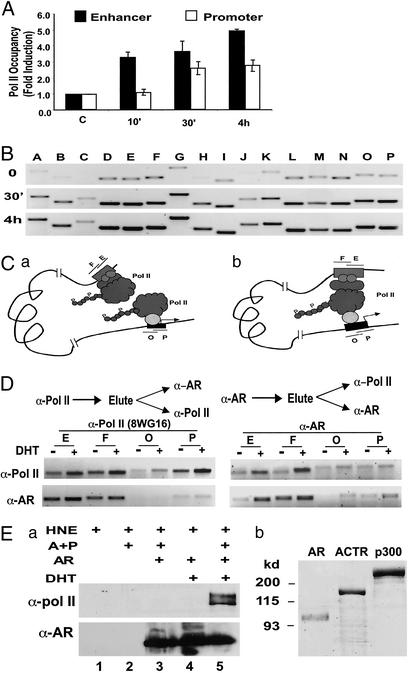
Figure 2.
Pol II is directly recruited to the PSA enhancer on androgen stimulation. (A) ChIP assay was performed with α-Pol II antibody (N-20) to analyze the Pol II occupancy at the enhancer (fragment E, filled bars) or the promoter (fragment P, open bars) of the PSA gene. The relative amount of Pol II occupancy in the presence versus absence of 10 nM DHT (fold induction) was determined by quantifying the PCR products obtained from three experiments. (B) Pol II occupancy over the entire PSA upstream regulatory sequence was analyzed by using ChIP assay as in A with the monoclonal α-Pol II antibody 8WG16. (C) Two possible modes of androgen-induced Pol II occupancy at the PSA 5′ regulatory region: Pol II is recruited to the enhancer and promoter independently (Left) or Pol II is recruited to the promoter and physically interacts with protein complex formed at the enhancer (Right). (D) Sequential ChIP assay was used to analyze the association of Pol II and AR at the PSA promoter (O and P) or the enhancer (E and F). LNCaP cells were treated with 10 nM DHT (+) or mock-treated (−) for 1 h before ChIP assay. Chromatin fragments were first immunoprecipitated with α-Pol II (Left) or α-AR antibody (Right). Immunocomplexes were eluted from the agarose beads and diluted for a second immunoprecipitation for AR or Pol II occupancy analysis. (Ea) Immobilized nucleosomal PSA enhancer fragment (−4500 to −3750) was incubated with HeLa nuclear extract (HNE), in the presence or absence of purified AR, ACTR and p300 (A+P) proteins shown in b, and DHT as indicated, followed by extensive washes and Western blotting with indicated antibodies. (b) Coomassie staining of purified AR (100 ng), ACTR (500 ng), and p300 (500 ng) proteins.