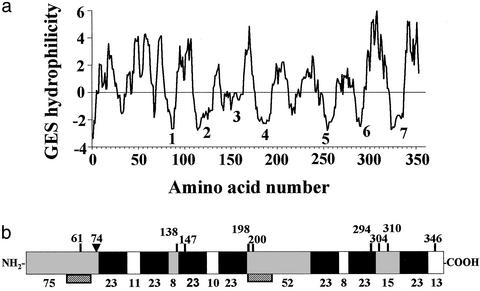
Figure 1.
Structural analysis of deduced amino acid sequence of putative mPR gene. (a) Hydrophilicity profile according to GES method (Goldman/Engelman/Steitz, 1986). (b) Schematic diagram of encoded protein showing extracellular (gray), seven-transmembrane (solid black), and cytoplasmic (clear) domains predicted by several programs. Vertical lines indicate potential phosphorylation sites. ▾, potential N-linked glycosylation site. Numbers above: amino acids from N-terminal end; numbers below: number of amino acids in each domain. Hatched boxes: peptide sequences used to generate polyclonal antibodies.