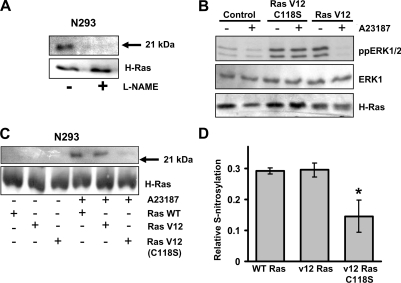
Figure 5. NOS-mediated S-nitrosylation of H-Ras.
(A) N293 cells were incubated in the presence or absence of 1 mM L-NAME for 18 h before the addition of 10 μM A23187. Cells were lysed and subjected to the S-nitrosylation assay followed by immunoprecipitation of H-Ras. The resulting biotinylated proteins were detected by immunoblot analysis with an anti-biotin antibody. Total H-Ras expression is included as a protein loading control. The results shown are representative of two independent experiments. (B) N293 cells expressing wild-type H-Ras, constitutively active H-Ras (Ras V12) or H-Ras G12V C118S (Ras V12 C118S) were treated with or without 10 μM A23187 for 2 h. Cell lysates were immunoblotted for active ERK1/2 (ppERK1/2), total ERK1 or H-Ras in the top, middle, and bottom panels respectively. The results shown are one representative of three independent experiments. (C) N293 cells transfected with wild-type H-Ras, H-Ras G12V (Ras V12), or H-Ras G12V C118S [Ras V12 (C118S)] were treated with or without 10 μM A23187 for 2 h. Following S-nitrosylation analysis using the biotin-switch assay, H-Ras was immunoprecipitated, and immunoblotted using anti-biotin and anti-H-Ras antibodies. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (D) The relative amount of S-nitrosylated H-Ras was quantified by densitometry. Results are means±S.D. for three independent experiments. * P<0.05. WT, wild-type.