Fig. 4.
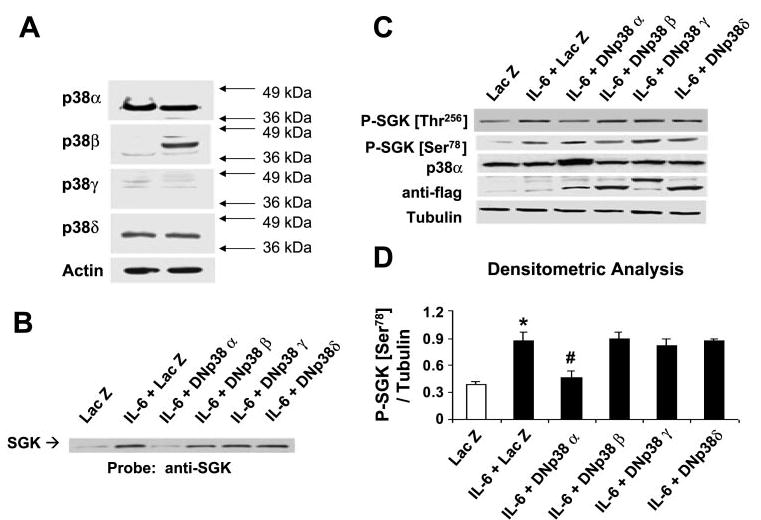
p38 MAPK isoforms are differentially expressed and selectively activate SGK in cholangiocarcinoma cells. A: cell lysates were obtained from unstimulated KMCH (left) or Mz-ChA-1 (right) cholangiocarcinoma cells. Protein (50 μg) was separated by SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was stripped and reprobed with antibodies specific for p38α-, -β, -γ, or -δ MAPK isoforms, or for β-actin used as a loading control. The results are representative of 3 separate experiments. KMCH cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged, isoform-specific, dominant negative p38 MAPK or LacZ-expressing control plasmids as described in materials and methods. After 48 h, cells were stimulated with 10 ng/ml IL-6 for 40 min. Cells were lysed, and an aliquot of the whole cell lysate was used for Western blot analysis, whereas nuclear extracts were obtained from the remainder. B: SGK expression in nuclear extracts was identified using an antibody against SGK. A representative immunoblot of three separate studies is shown. Dominant negative p38α decreases nuclear translocation of SGK. C: immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysate using an antibody against phospho-Ser78 SGK. The same blot was reprobed with specific antibodies against phospho-Thr256 SGK, p38α MAPK, FLAG, and α-tubulin. Expression of dominant negative (DN) constructs was confirmed using anti-FLAG antibodies. D: expression of phospho-Ser78 SGK was normalized to α-tubulin and quantitated with the use of NIH Image software. The means ± SD of densitrometric analysis from 3 separate determinations are shown. Dominant negative p38α selectively decreases phosphorylation at Ser78. *P < 0.05, compared with LacZ control group. #P < 0.05, compared with IL-6-treated LacZ group.
